Updated: 15-Jan-2019
See General Motors for main information and the list of engines.
This well-known American automotive company saw its engines adapted for amateur construction, in innumerable examples.

General Motors logo
-Besides the well-known contribution during WWII, it made a 4-cylinder, radial engine known as the "U-type". The cylinders were arranged radially. It was the R-250-1 and -3.
-The R-250-3 was supercharged. Their military version was the X-250D, designed in 1943 by GM's Research Laboratory. They were tested on Cessna aircraft.
-They were liquid-cooled, 2-stroke engines. The maximum power was 200 hp at 2,275 rpm, with gearbox. The dry weight was 275 lbs.
-As we have seen, GM, as a large industrial organization, brings together Allison Division and Detroit Diesel Allison (now Rolls-Royce).
-The adaptation of automobile engines is substantial although it can be said that all have been carried out experimentally.
-Pinto and Chevrolet engines were installed on small aircraft, and in the illustration below we can see a Corvair 6-cylinder with a displacement of 2,687 cc, giving 115 HP at 4,400 rpm, installed on a small plane.
“Corvair on board”
-George Morse was an example of these GM-engine adaptations, with his Auto Aviation Olds (from Oldsmobile) that boosted his Skybolt and Prowler planes. The same for Steve Williams and his Tailwind.
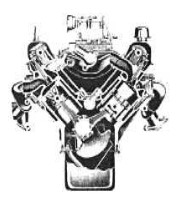
“GM 215”
-The Pontiac, Oldsmobile and Buick 215 hp engines with "Jetfire" turbochargers and aluminum blocks, were highly appreciated.
From Appendix 6: During the First World War, in 1918, Buick (GM = Cadillac + Buick) presented the water-cooled L-12A Liberty.
-The engine in the below photograph (NASM File) became known as the Model A Buick and was mounted on the Fokker T-2.
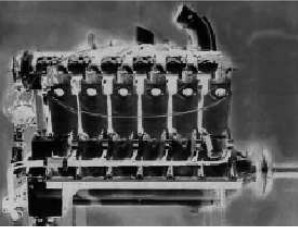
“Liberty L-12A made by Buick” (PiP)
-We located a General Motors radial engine intended for the Pontiac X-4 experimental car. This engine is mentioned as model X-250 in the main text.
-In the documentation where the information was obtained it is said that the X-4 car engine is a derivative of the X-259 engine in turn derived from the X-250. The X-259 is considered the grandfather of the X-4 engine, so the X-250 would be a great-grandfather.

“The Pontiac X-4 with radial engine”
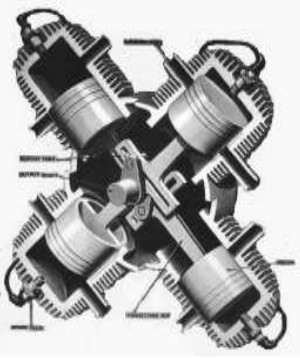
“X-4 engine with rigid rods”
-As we see, connecting-rod system and pistons act as shuttles like in the Bourke engines.
-GM developed this engine jointly with Williams International (see) to be used as APU, auxiliary generator and possibly for cruise missiles. It is proclaimed for high fuel efficiency.
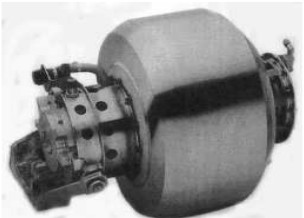
“GM-Williams small turbine”
From appendix 13: Adaptations of the powerful General Motors car engines continue to appear.
-A new proof is the 620 hp Bigblock engine for the agricultural "Airtractor" aircraft. The conversion is done by EPI Inc.

“Bigblock on a test bench”
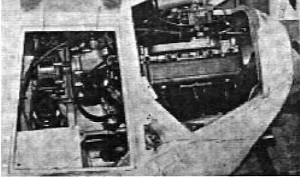
-From the GM "Kuva" vehicle there is a conversion of its LS-3 block for a Cessna C-172 aircraft.


“Two photographs of the Kuva LS-3 on a Cessna C-172”

"Curious LS-1 engine with double exhaust pipes"
-The double exhaust pipes can be destined for a WWII fighter jet replica.
-Below we show another version of a GM block LS-1 engine for another application.

“LS-1 with a Geared Drives gearbox”

“LS-1 Adapted with Rotator gearbox”

“Like the V8, V6 engines are used as well”
Engines of GM
We have no more detailed engine information for this brand. We continue our search. Any help will be appreciated.


