Updated: 08-Jul-2020
KHI, is Kawasaki Heavy Industries, but its correct name was Kawasaki Kokuki Kabushiki Kaisha, installed in Hyogo, Kobe. It was founded in 1918.
-Today it is known as Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha, manufacturer of motorcycles and industrial engines, of which for example the KAE-240 engine with 6 horizontally opposed cylinders has been directed to general aviation. It gives 240 CV at 3,000 rpm and 260 CV at 3,400 rpm. This engine was manufactured between 1956 and 1960.

“Kawasaki Ka-92 aircraft”
-Between 1927 and 1940 Kawasaki manufactured BMW VI engines with 12 cylinders in V giving 500 CV nominal. They were built under license and mounted on the Ka-92.
-They also made the BMW engines with 600 CV that became increased up to 800 CV. The Ha-9-IIa was a derivative of this engine and gave 850 CV at takeoff.
-The supercharged Ha-9-IIa gave 950 CV at 3,800 meters of altitude.
-The BMW VII was a BMW VI that was improved to 750 CV, and was also manufactured under license.
-Like the Ha-9-I, it was an 12-cylinder inverted Vee-engine that delivered 850 CV, the same as the Ha-9-II-ko.
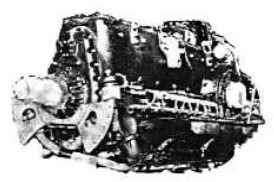
“Ha-40”
-In 1939 Kawasaki acquires the license from Daimler Benz for the construction of the inverted 12-cylinder DB-601, known as the Kawasaki Ha-40 that was mass-built by the Japanese during WWII. It was installed on the "Tony", with 1,100 CV. See Aichi too.
-In the army it was known as Type II and in the Navy as Type 22 (Ha-60). The Ha-140 did not result, and did not enter into production.

“Ki-64 aircraft”
-The Ki-64 aircraft, with a special design, consisted of two coupled Ha-40 engines, resulting in the Ha-201, with one engine in front of the pilot and the other one behind him. The rear engine shaft passed inside through the front propeller shaft.
-It drove two 3-blade contra-rotating propellers: the rear propeller had a fixed pitch and the front one a variable pitch.
-It was a test engine without continuity. This engine gave 2,350 CV in total.
-Kawasaki also manufactured the Nakajima 99 with 1,500 CV, an air-cooled, 14 cylinder engine. It was built under contract for the Army.
-Towards 1953, it carried out engine revisions and repairs in the Akoshi factory for the USAF and the JDA, like the Allison J-33, Westinghouse J-34, RR Orpheus and GE J-47.
-From 1967 they manufactured the AVCO Lycoming T-53 under the designation KT5311A and KT5313B, then towards 1985 the T53-Kawasaki-13B and T53-K-703, as well as the T55-K-712.
-Kawasaki collaborates in the manufacture of parts for the RR Adour, PW F-100 and JT8D, IHI-T56 and with the IAE, develops and manufactures the V-2500 airline engines.
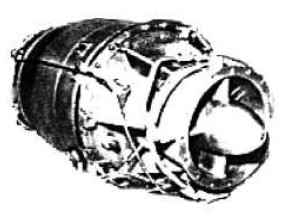
“KJ-12”
-They have also manufactured a small turbojet for RPV’s, around 1979, with a centrifugal compressor, single turbine and annular chamber.
-It gave 331 lbf of thrust, it was the KJ-12.
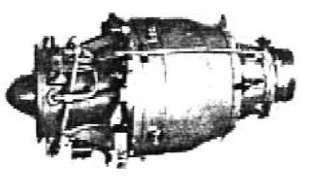
“KJ-12”
-During the 1970’s and 1980’s, Kawasaki motorcycle engines have been adapted to motorgliders, ULM, experimental aircraft, etc.
-Especially the 340 and 440 engines.


“Kawasaki 340, two models”
-The Kawasaki 340 is air cooled with two cylinders, and one carburetor.
-The upper one has manual start by puller.
-They give a little bit more than 30 CV. They are lightweight as they are between 39 and 45 kg.
-The 440, in the A version gives 43 CV and is air cooled. We show an air-cooled one with cooling by natural air flow and the other one with forced air flow by a fan.
-The 440-B variant can deliver 48 CV. with CDI Ignition as above. The cylinders have nickel finish.

“Kawasaki 440-A”

“Kawasaki 440-B”
-The 440-C, gives 55 CV with two carburetors and it weighs 70 lbs.
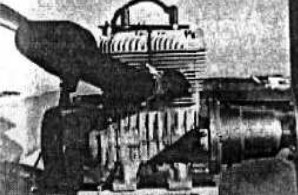
“TA-440A”
-The TA-440B that gives 52 CV is used for ULM. It is an air-cooled, 2-stroke, twin-cylinder engine.
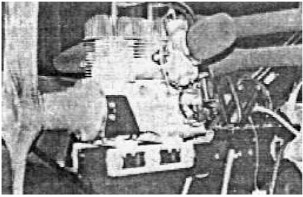
“TA-440B”
-The TC-440 is liquid cooled and can related to as TC-440A or TA-440C, according to different documentation.
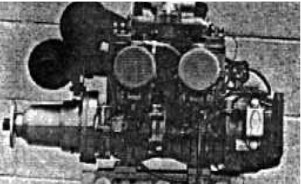
“TC-440”
-Other Kawasaki engines are offered such as the liquid-cooled 440 and 500, and an air-cooled 650. All three give about 60 CV of power.
-And there was another one with less fortune, the 3-cylinder, 2-stroke engine that gave 50 CV.

“TA-440”
-The TA-440 with 2 cylinders, like the one installed on a Mitchell B-10 motorized hang glider, is cooled by forced air by a fan. It delivers 38.5 CV.
-The TA-440A, with 38 CV, has reduction gear 3.1: 1 or 2.1: 1, on demand.
-The truth is that it belongs to the Kawasaki “Invader” 440 motorcycle, giving 65 CV at 7,800 rpm.
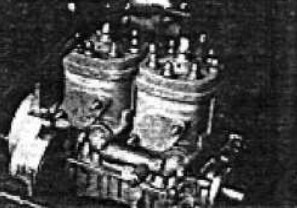
“TC-440A”
-The geared version reaches 72 CV. Type TC-440A ”.
From Appendix 6: The engines mentioned in the main text are being installed on light aircraft, ULM, trikes, etc.
-For example the Kawasaki 340, in inverted position for this motorized hang glider.

“Kawasaki 340”

“Kawasaki 440, half mounted”
-This model is already presented in the main text and used on Snowmobiles and also on ultralight aircraft.
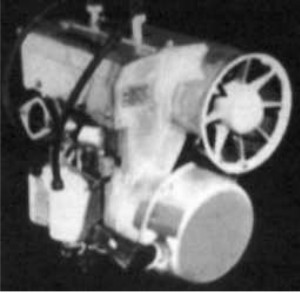
“Aspect of the one known as Arctic Cat”
-The architecture of this engine is repeated in many other brands, starting with the Kiekhaefer.
-Others are Cuyuna, the Polaris (Fuji), the Canadian Curtiss-Wright CCW (Kyoritau Noki), Bombardier (Rotax), JLO (Rockwell), Evinrude, Mercury (Kiekhaefer), Gotbrud, Moto-Ski (BSE Taiwan), etc.
From Appendix 9: From the Tokoruzawa Museum, my collaborator Talo Shi sent me a photograph that seems to be of the Ha-40 model, a Japanese copy of the DB-601.

“Ha-40, damaged and inverted”
-The author loves the valve control mechanism consisting of one rocker with rollers that controls two valves with a single cam, the intake and the exhaust valves.
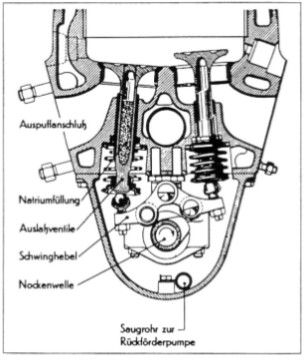
“Detail of the cam mechanism”
-And an 800 CV engine that is a BMW Type 40 variant (C-9-IIB). It is made in 1938.

“Kawasaki Type 40”
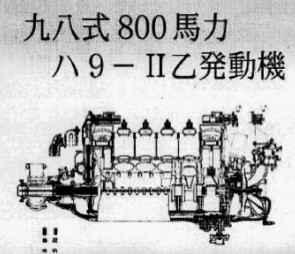
“Kawasaki Type 40, oil circuit”
-It is a 12-cylinder Vee-engine built under license.
From Appendix 10: We received new information on an air-cooled engine of this brand for ultralights, etc.

“Kawasaki 3440”
-It has belt-gear reduction, very wide.
Engines of KAWASAKI
Model: 340, 2 cyl, 30 HP
Arquitecture: 2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 30 CV
Weight: 40 Kg

"Kawasaki 340, fig. 2"
Model: 3440
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:

"Kawasaki 3440"
Model: 440
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 43 CV
Weight:

"Kawasaki 440-A"
Model: ”99”, Nakajima Lic.
Arquitecture: 14-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: Ha-140
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Ha-201 (2x Ha-40)
Arquitecture: 24-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 2350 CV
Weight:
Model: Ha-40 (DB-601A, Lic)
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 1100 CV
Weight:

"Kawasaki Ha-40"
Model: Ha-9 (BMW VI, Lic)
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: Jupiter (Lic. G-R/Bristol)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Kae-240, 6 cyl. boxer 240/260 HP
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 240 CV @ 3000 rpm
Weight:
Model: KJ-12
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s: centrifugal compressor
Combustion chambers: Annular combustion chamber
Turbines: Single-stage turbine
Power / Thrust: --- / 331 Lbf
Weight:

"Kawasaki KJ-12 fig. 2"
Model: KT-5311A, (Lic. Lyc. T-53)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: KT-5313B, (Lic. Lyc. T-53)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:


