Updated: 22-May-2025
It's 'Tsentralniy Institut Aviatsionnogo Motorostroeniya' or the Central Institute for the Development and Construction of Aeronautical Engines. Sometimes simply referred to as IAM.
- Bessonov was the one who designed an engine at the Center, the MM-1, with 250/300 hp and general lines similar to the DeHavilland Gipsy Six. Year 1936.
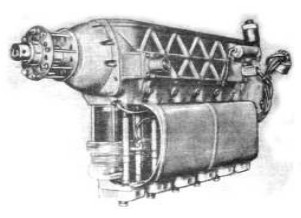
“MM-1”
- The MM-2, was an inverted, air-cooled V12 giving 450 hp.
- The VAD-2 and VAD-3, delivered 30 hp and 45 hp respectively. They were small geared, air-cooled engines with inverted inline 4 and 6 cylinders.
There were other lesser-known projects, such as a 24-cylinder H-engine around 1931.
More recently, there are projects such as the IZh engine from the TsIAM Motiv group, known as the 700, giving 60 hp.
It had two water-cooled, in-line cylinders.
According to a publication it has a reduction gear, although it is not visible.
From the same group, the DD-700/45R model is known, a 45 hp engine with two air-cooled, horizontally-opposed cylinders.
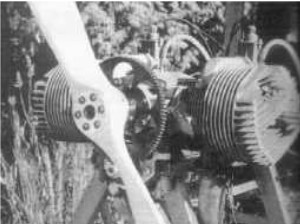
“D-700/45R engine”
Engines of TsIAM
Model: DD-700
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: H-24
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: IZh (Motiv-700)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: MM-1
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: MM-2
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: VAD-2
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: VAD-3
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:


