Updated: 21-May-2025
TRW is a company group dedicated to the development of defense and space projects and systems. Also known as TRW/STL, for Space Technology Laboratory, located in California.
-TRW is a manufacturer of large launcher engines and small maneuvering engines.

“TRW, TR-201 silhouette”
- The most well-known and powerful engines are the TR-106, TR-107, and TR-201.
- The first, also known as LPCE, has a thrust of 295,000 kgf and runs on LOX/LH2.
- The TRW TR-107, built in 2002, operates on LOX and kerosene, and has a thrust of 500,000 kgf in a vacuum.
-And the TR-201, the lightest of them, with a thrust of 4,270 kgf, is used on the upper stages of the Delta P and on the Lunar Module spacecraft of the Apollo project.
-Other projects have included the MIRA, a hypergolic, liquid-fueled, variable-control rocket engine.
“TRW, MIRA”
-This brief overview covers the maneuvering engines used on the Lunar Module, based on hydrazine, and those used on the Mariner missions to Mars in 1969.
-TRW's product range includes mono- and bi-propellant engines, colloid-based, ionic, radioisotope, and electrothermal engines.
-The most commonly seen hydrazine-based thrusters are the MRE-5, giving 3 kgf, and running on N2O4/MMH.
-The 9 kgf hydrazine MRE-15/OMVs giving pulses of 0.020 seconds, capable of firing 100,000 times or cycles.
-The OMVs are variable thrust engines.
-One of them has a thrust of 58 kgf and uses dual fuel: N2O4/MMH

“Technicians with the mid-course Mariner"
-The TRW rocket engine test base is located in San Juan Capistrano, California.
From Appendix 6: Solid-fuel rocket engines have the advantage of easy storage and rapid firing without preparation.
-The TRW Company, at its Propulsion Systems Center, successfully tested a new type of engine with gel-like fuel, with the same advantages as solid fuels.
-But another additional advantage of gels is that they can be stored in tanks and flow through conduits to be loaded into the engines. They are not cryogenic.
-We know that solid fuels are usually perishable and are molded, and when their effectiveness expires, they are either fired or destroyed.
-Gel engines don't have this problem. If the fuel expires, it does so in the storage tanks. Costs are certainly reduced.

"TRW Gel Engine"
From Appendix 9: Rocket Engines, add or check.
-SEYST
-SEPS
-TR-106
-TR-107
-TR-202
-LPCE (TR-106)
-MRE-15/OMV
-MRE-5 / CO
-OMV
-MON (apogee)
-PRESS-Fed, -1000K, -200K, -25K, -5748K
From Appendix 10: TRW (Northrop Grumman Space).- USA. This brand name refers to: MIRA, URSA, Apollo Lunar Module Engine, Sentry Kew, TR-series, FMT, Mariner, LMDE...
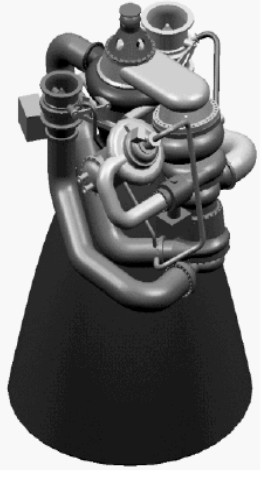
“TR-107”
-Also the Oress, Fed., SEPST, MON, OMV, MRE...
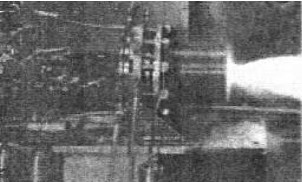
-The TR-201 is a derivative of the LEMDE (Lunar Excursion Module Descent Engine).

“TR-201”

“TRW MIRA 150A”
-The small MIRA engines had variable power control. There are three models: the 150A, which delivered thrust between 30 and 150 lbf, built by JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory).
-The MIRA 500, with thrusts from 25 to 500 lbf, and the MIRA 5000, from 250 to 5,000 lbf.
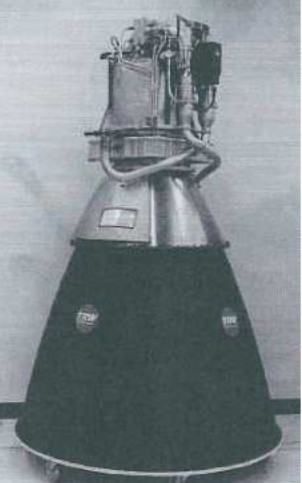
“TRW Apollo LMDE”
-The LMDE was built around 1963 for NASA/Grumman.
-Another TRW engine series was the URSA, a family of small engines for universal use in space applications.
-These engines were manufactured in 1966, and there were three models: the URSA 25R, the 100R, and the 200R.

“URSA 25R, 200R y 100R”
-These engines have been used on Gemini, Apollo, Dyna-Soar, and the Manned Orbiting Laboratory, among other systems.
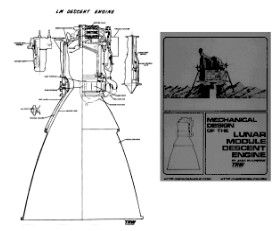
“TRW LMDE, cross-section”

“Checking an LMDE Engine”

“TRW LMDE Engine”
Engines of TRW
Model: Apollo Lunar Module, descent engine
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: LMDE
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: LPCE
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: MIRA
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: MON/Hydr., Dual mode apogee
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: MRE-15/OMV
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: MRE-5 / Compton Obs.
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: OMV (Variable Thrust eng.)
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Press Fed, -1000k, 200k, 25k, 5748k
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Sentry Kew
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: SEPST
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: TR-106
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: TR-107
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: TR-201
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: TR-308
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: TR-40
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: URSA 25R, 200R, 100R
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:


