Updated: 11-May-2021
(See Henry Potez).
Mr. Henry Potez was an airplane builder well known for his machines, but he also built engines.
-In 1926 he had the opportunity to acquire the Anzani brand.
-He immediately created the “Labotaroire D’ Etudes de Moteurs ”within his own company in Suresnes.
-The first thing was to modernize and continue building the Anzani engines that were in use at that time.
-In 1930, there was the 100 CV Potez 6A.

“Potez logo”

“Potez 6A”
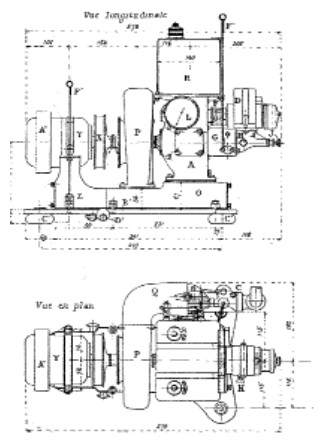
-It had 6 cylinders, the result of joining two radial rows of 3 cylinders each. The exhaust manifold was at the front.

“Potez 6Ab”
-The 6Ab, without the front exhaust manifold.
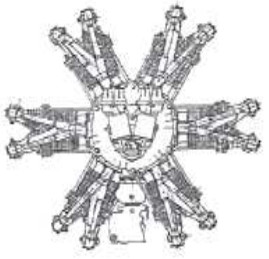
“Potez 6Ab rear diagram”

“Potez 6Ab, side view”
-The Potez 3B that gave 60/70 CV -on the Potez 60 plane, for example-, is like a half 6A engine from 1932.

“Potez 3B”
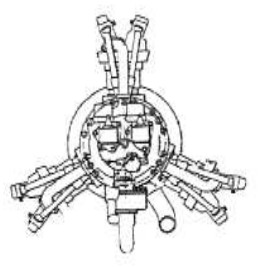
”Potez 3B, rear schematics”
-The 6B model was very similar to the 3A but more powerful, and gave between 120/140 CV. (6Ba, 6Ab, 6Ac, etc, were a double 3B).

“Potez, 6B”
-We see here that the cylinder located at "3" (on the dial of a watch) is further back than the one at "1" and the one at "5".
-We also see that the exhaust pipe of the "3" is longer than those of the previous ones.
-Therefore the engine is a double row with 3 cylinders each.
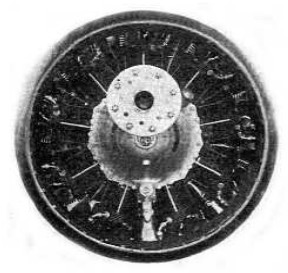
-Much earlier, in 1920 Potez made an engine whose approach breaks with the known.
-It was installed on the Potez VIII plane.
-It was installed in an unusual way as it was fitted with a vertical crankshaft and a 90° bevel gearbox that coupled its output shaft to the propeller. It was air cooled.
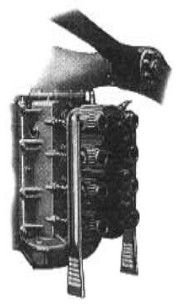
"Potez engine on airplane VII, 1920"
-Continuing with the previous thread, we come to the 9-cylinder radials.
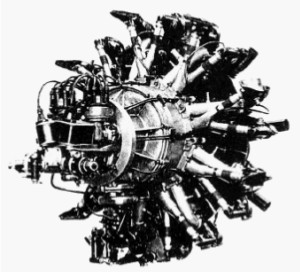
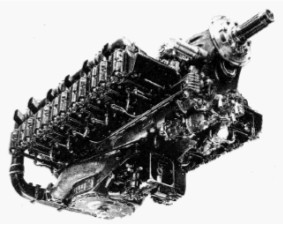
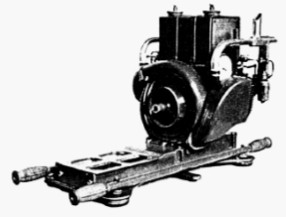
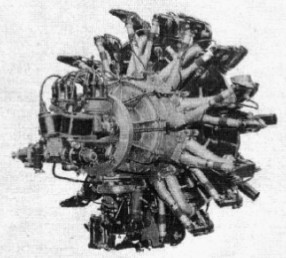
-There were the 9A, 9B and 9E models. The first one was the 9A that gave 180 CV.
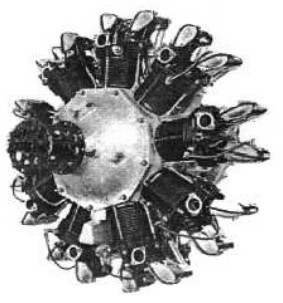
“Potez 9A”
-The superimposed gear was also mounted on the 250 CV Potez 9Abr, rotating at 2,700 rpm, that is, a slightly higher speed than the 230 CV 9Ab at 2,300 rpm.

"9Abr with superimposed gear"

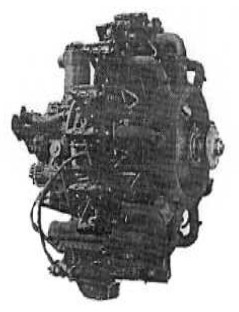
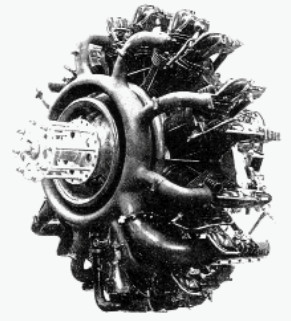
“Potez, 9B”
-The 9B gave 220 CV at 2,400 rpm. Below we see it installed on the Potez 53 aircraft.

“Potez 9B” (PiP)
-In this review we provide the Potez 9C-01 engine, the characteristic of which is that it uses superimposed gear in the way of the English Pobjoy.
“Potez 9C-01”
-The Potez 9C-01 was based on the 9Ab and gave 220 CV at 2,500 rpm.
-Around 1936 the 9E appeared, with 225 CV, and nine radial cylinders. Below we see a photograph of the 9E, not very clear, but real.
“Potez, 9E”

“Potez 9E”
-The photo of the 9E is included to see this engine better, since in the original text it is somewhat dark.
-From the Anzani range, the time has come for the LEM (the Laboratory) under the orders of designer Menetrier, responsible for the modernization of those engines, to start a new range of engines with in-line cylinders.
-In the same year 1932 he was already working on 4, 6, 8 and 12 cylinder engines. The A-4 with 50 CV did not work out.
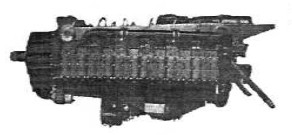
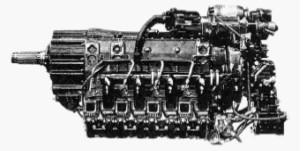
-In the years 1932 to 1935, and in collaboration with Rateau, the Rateau-Potez 12As was made. It gave 350 CV at 2,400 rpm and later reached 420 CV. It was water cooled and turbocharged.
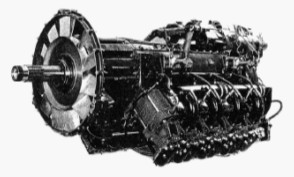
“Potez, 12D.30”
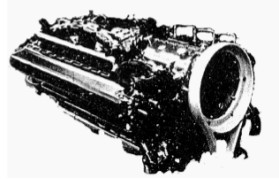
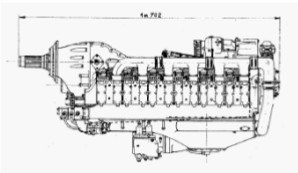
-We provide an impressive view of the of 500 CV Potez, model 12D00, with 12 horizontally-opposed cylinders. It was designed in 1937.
-In fact it is a "cannon engine", with an elevated gearbox for this purpose. The bullet was fired through the hollow propeller shaft.
-A mechanical supercharger is located under the engine and attached to it the carburetion system.
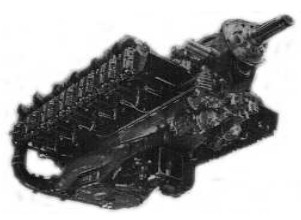
“Potez 12 D00”

“Potez 12.00-3 at the MAE”
-Potez made the 12.00 with two reducer types, one with superimposed spur gears as in the photo above, and the other with the epicyclic concentric as we see below in the photo of a Potez 12 D-30.

“The opposed 12-cylinder gearbox”
-A 6-cylinder inverted in-line immediately appeared, with identical cylinder sizes for the 6, 4 and 8-cylinder inverted V engines.
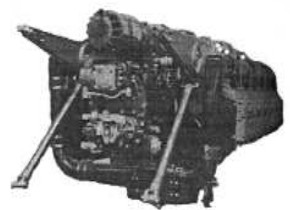
“Potez, 12D.30”
-In the case of the water-cooled 12 V, it did not come out, and some did not go to the production line, which is the case of the 12D with twelve horizontally-opposed cylinders that we show here in 3 illustrations.
-The 12D.30 was air-cooled with a built-in supercharger and gave 410 CV.

“Potez, 12D.30”
-The 12D.30 reached 650 CV at 2,800 rpm. The engine was made from 1936 to 1950.
-There also was the 12D.40 engine, from the years 1950-1953 with a planetary gearbox from 0.657 to one and the supercharger rotating at 8.75 times the crankshaft speed. It had fuel injection.
-There are no known applications of the Potez 12D.30 or 12D.40 engines, nor flight tests.
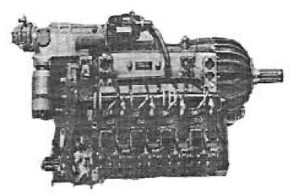
“Potez 8 inverted V”
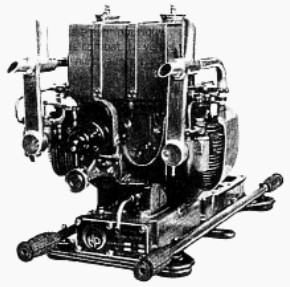
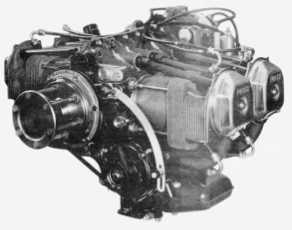
The 8-cylinder, inverted-V engine was known as the Potez 8D giving 360 CV, and appeared in 1937, the same as the 12D.
-Really nice, it has epicyclic frontal gear.
-The 8Do of the above figure already gave 450 CV. Later we will see its evolution.
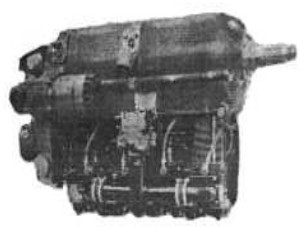
“Potez 4D.01”
-Inverted 4-cylinder in-line engines such as the 4D.01 have been used on a number of French training aircraft such as the Nord, among others.
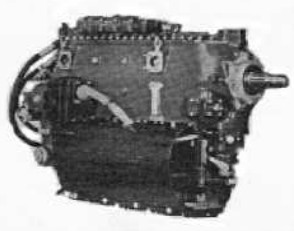
“4D.30”
-The basic 4D.30 gave 240 CV weighing 180 Kg.
-It had a mechanical supercharger installed in an unusual way, above the engine's crankcase in a flat position.
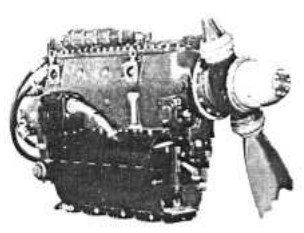
“Potez 4D.32”
-The supercharger shaft goes through the crankshaft block to engage with the drive mechanism of the latter.
-The 4S.32 also gave 240 CV. In the case of the 4D.34 from 1948 the power was reduced to 220 CV.

“Potez 4D.34”
-These engines have been used on the Nord military training aircraft (on ESALAT, for example), with acrobatic capacity and that replaced the previous “Stampe”.

“The 4D.30 at the MAE”
-Two photographs taken at the reserve stock at the Paris Air and Space Museum are shown.

“Potez 4D.34D at the MAE”
-The mechanical supercharger is unusually located on top in a horizontal position.

“Supercharger cutaway”
-The new 8D.30 engines also appear with new gearboxes and here we can see some models with and without deflectors.

“Potez 8D.30.01”
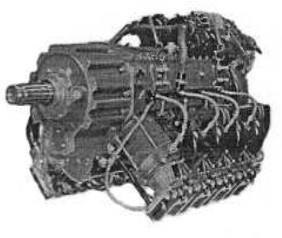
“Potez 8D.30”
-And with benches and fireproof plates, the following models -32 and -34.

“Potez 8D.32” (PiP)
-During the German occupation, Mr. Menetrier was commissioned to build very high-power engines.

“Potez 8D.34”
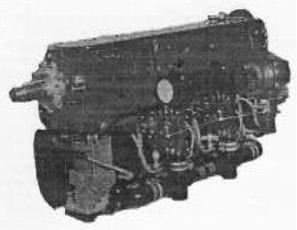
“6D.00”
-In 1946, the 6D with 6 inverted in-line cylinders and in the order of 240 CV came out.
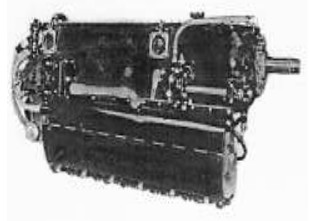
“6D.02”
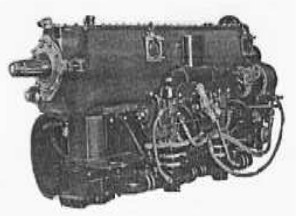
“Potez, 6D.02”

“6D.02A at the MAE”
-Soon the 305 CV version would be released in the 6D.30 version, supercharged as in the 4D, incorporating a compressor upon the block and whose ducts and collectors we see in the below illustration.
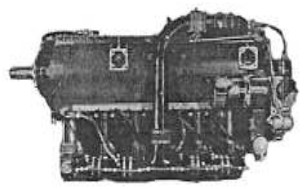
“Potez , 6D.30”
-Since 1949 Potez was located in a renovated facility in Argenteuil.
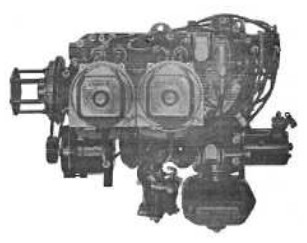
“Potez, 4E.00”

“Potez 4E.00, at the MAE”
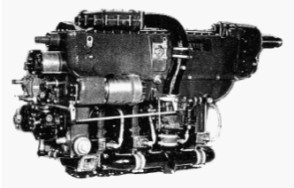
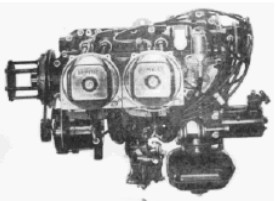
-They were planned to be used in general and sport aviation. Expanding at the end of the 1950's, the Potez 4E comes out with powers between 90 and 117 CV.
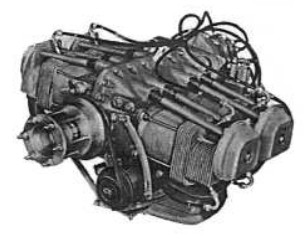
“Potez, 4E.00”
-The 105 CV Potez 4E.02 comes out in 1952. It had four horizontally-opposed cylinders, and the entire layout including the size were similar to that of its American contemporaries with the intention of being used as a “retrofit”.
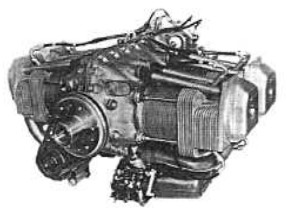
“Potez, 4E”
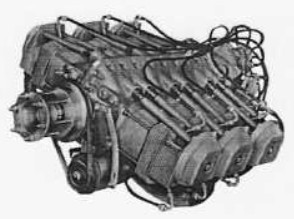
“Potez 6E.00”
-The most characteristic of the 4E was its ignition system that consisted of a double ignition, one magneto and a delco (therefore dependent on a battery).
-The 4E.20 giving 105 CV at 2,750 rpm that was made from 1960 to 1965 was widely used in France in multiple airplanes since it was built in a certain quantity, from Jodel, Jurcá, Morane Reims, Mascaret, Scintex, etc.
-The Potez 4E.30 gave 117 CV and had fuel injection. It was used quite a bit too.
-The E6.30, with 6 opposed cylinders, delivered 175 CV at 2,800 rpm. They were built from 1961 to 1965.
-In 1963, the H. Potez company concluded an agreement, bringing Avco Lycoming into its company. The following year the engine section is canceled.
-A maneuver that we have seen in other cases and not only in aviation.
-As the end of this chapter, we have to mention that by 1934 Potez provided on-board auxiliary engines, the well-known APP and the ground APU.
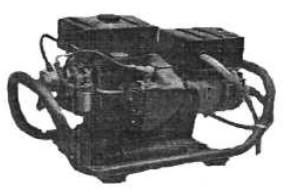
“Potez APU”
-With their generators they provide electrical energy for radios, main engine starters, or with a compressor for tire inflation, pneumatic starters, etc.

“APU 1C, without accessory”

“APU 2C”
-The 1C model is a 1 CV single cylinder aux. engine for a 450 Watt generator.
-The two-cylinder 2C gives 2.5 CV for a 1200 W generator, or the single-cylinder 1D gives 1.5 CV with a compressor for 25 Kg/cm2, pressure and vacuum or a 600 W generator.

“APU Potez 1D”
From Appendix 6: We got a more complete picture of the rare vertical motor that appears in the main text. (From the Flight archive).
- It was presented at the Paris Motor Show on the Potez Type VIII aircraft, it is a four-cylinder engine with T-combustion chambers, that is, with a valve on each side of the cylinder.
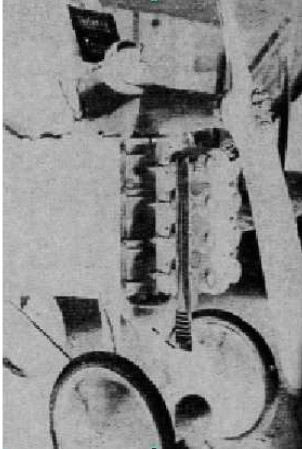
“Potez engine” (PiP)
From Appendix 7: We obtained more information from the brand via AAMS.

“Two-tone color logo”
“New photo for the 9Ab”
-The 9Ab increases its power compared to the 9A due to the increase in the compression ratio from 5.5 to 6 to 1. It appeared in 1934.
“Potez 9Ba, rear view”
-In 1933, the 9B model was specially made to participate in the Deutsch de la Meurthe Trophy. The one in the upper illustration is a 9Ba and bel,ow it the 9Bb of the following year (1934). It reached 350 CV.
“Potez 4D34”
-The 4D34 is an evolution of the 4D30 and is slightly more powerful. In the 4D34, the reducer stands out, this time with superimposed gears. It maintains the compressor on top of the engine in a characteristic position.
-From a Potez brochure we have two new views of the 8D30 with 450 CV of maximum power and another view of an 8D32 with fan for forced cooling.
“The Potez 8D30 and 8D32”

“Two photos of the 12 As”
-The Potez 12 engines belong to a new generation, started in 1932 and presented at the Paris Motor Show.
-The 12As model has a Rateau turbocharger.
“12D03 photo”
-Around 1940, the 12D03 was approved, but it was not put into service due to the beginning of the German invasion.
"Potez 12D03, schematic drawing"
-The Potez 12D03 engine gave between 480/575 CV. The latter power is with a supercharger.
-Potez created an engine development laboratory in Suresnes from which the 8D and 12D engines came out.
-This laboratory was founded in 1937 after Lorraine's nationalization that same year.
-At this Laboratory, there was an engine project, which turns out to be massive as it had four radial 7-cylinder rows. This was the turbocharged 28D engine.
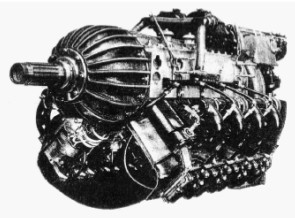
“Potez 8D.00 engine”
-The 8D.00 is mentioned in the main text but no illustration is shown and now we are able to show one.
-Below we show a Blue-Print for the A-4 engine designed by Coroller. For this reason it was known as Potez-Coroller.
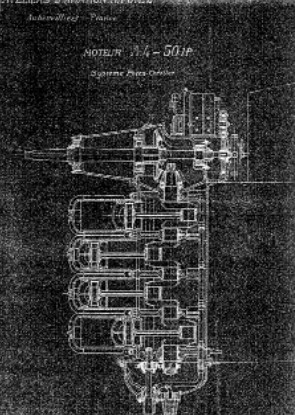
“Potez A-4 engine with vertical crankshaft”
-Two more engines that are mentioned in the main text and of which we now have illustrations are included in this extension: these are the Potez 4E20 and 6E30.
-The 4E was less powerful than the 4D. It gave 105 CV and weighed 94 Kg.
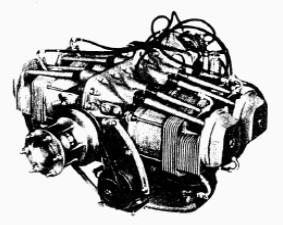
“Potez 4E-20”
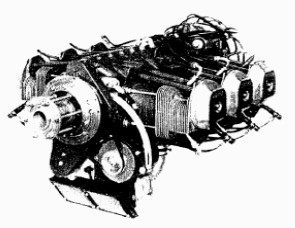
“Potez 6E-30”
-We also have recovered some illustrations of the on-board auxiliary engines.
-Below we show a plan of the 1C with a single cylinder that is cooled by a forced-air fan. The cylinder is placed horizontally to one side.
“Potez APP, model 1C”
“The Potez 2C Auxiliary Power Plant”
“Potez 2C seen from the other side”
-The 2C auxiliary power plant consists of two horizontally-opposed cylinders, air cooled by a centrifugal fan. If the 1C gave 1.11 CV at 4,500 rpm, the 2C gave 2.5 CV.
-They were followed by the 1D-3 models with 2 CV, the 2D-2 with 6 CV and the 2D-5 with the same power.
-They could be fitted with a generator capable of starting the main engines, driving fuel and oil transfer pumps, etc.
-They also could drive bilge pumps on seaplanes, compress air to refill bottles, de-ice, power the autopilot instruments, or drive hydraulic actuators.
From Appendix 9: From the maintenance manual we took the side and rear views of the Potez 4E.00 engine that we show below.
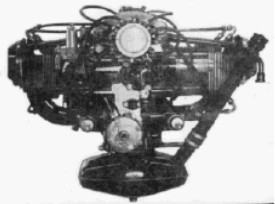
“Two Potez 4E.00 engine views”
-In the rear view we see the ignition system distributor by Delco. This is how engines were in the 1960's.
From Appendix 10: Interesting drawing of the 8-cylinder, inverted-V 8D model engine. See main text.

“Nice Potez inverted V engine”
- The radial engine model of this brand had a reasonable reception. It was used in the early 1930's in high-performance and racing aircraft (such as the Deutsch de la Meurthe Trophy),

“Potez 9B”
“The same engine from behind”
From Appendix 12: We found some more engine pictures of this brand.
“Potez 4E-20”

“4E-30, from behind with M-Delco system”

“4E-30, bottom view”
-We can see an oil collector in the lower rear part .
-Below we continue with a list of this brand's engines we have recently found.
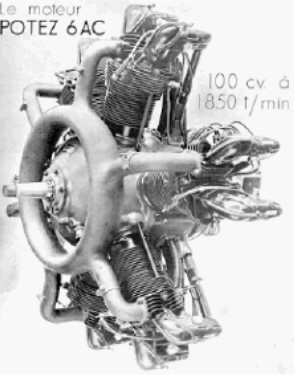
“Potez 6AC from a catalogue”
-The 100 CV Potez 6AC was a double row radial with 3 cylinders each. Two additional studs on each cylinder “tighten” them to the center crankcase. At the base of the cylinders there are no fasteners, nuts or studs, usual in these engines.
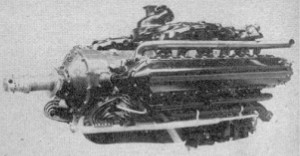
“Potez 12 AS”

“Potez 6 AC cylinder without base anchors”
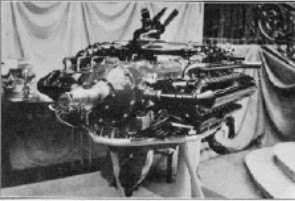
"The 12 AS at an exhibition"


“Potez 6E-30”
-The 6E-30 has 6 horizontally-opposed cylinders and maintains the same structure or architecture as the 4 cylinder.
-We also see the M-Delco ignition system, and the double carburetor and double air filter calls our attention.
-We have a new photo of the Potez 9B radial engine and also of that engine with a very rare architecture for light aircraft, the one that has in-line cylinders and a vertical positioned crankshaft with cylinder heads facing the direction of travel.
-It is coupled to the propeller shaft with a 90° bevel gearbox.

“Potez 9B”

“Potez-Coroller on Potez VIII airplane”
-The engine is designed by a certain Coroller, hence the compound name by which this powerplant is known as well.

“Potez airplane with Coroller engine” (Arch. J.A)
Engines of POTEZ
Model: 1-C, -D3, (APP’s)
Arquitecture: Single-cylinder
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 1 CV
Weight:

"APU 1C, without accessories"
Model: 12-AS
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 350 CV @ 2400 rpm
Weight:

"Potez 12As, fig. 2"
Model: 12-D-00, -03, -30
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 500 CV
Weight:
12D.30: 650 CV at 2800 rpm.

"Potez 12 D00"
Model: 2-C, -D2, -D3, -5, (APP’s)
Arquitecture: 2-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 2.5 CV
Weight:

"APU 2C"
Model: 28-D
Arquitecture: 28-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: 3-A, -B
Arquitecture: 3-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 70 CV
Weight:

"Potez 3B"
Model: 4-D-30, -34
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 240 CV
Weight: 180 Kg
4D.32: 240 CV
4D.34: 220 CV.

"Potez 4D.01"
Model: 4-E-20
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 117 CV
Weight:
4E.02: 105 CV.
4E.20: 105 CV at 2,750 rpm.
4E.30: 117 CV

"Potez, 4E"
Model: 6-A
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 100 CV
Weight:

"Potez 6A"
Model: 6-B
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 140 CV
Weight:

"Potez, 6B"
Model: 6-D, -00, -30
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 240 CV
Weight:
6D.30: 305 CV.

"Potez 6D.00"
Model: 6-E-30
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 175 CV @ 2800 rpm
Weight:

"Potez 6E-30, fig. 1"
Model: 8-D-00, -30, -32
Arquitecture: 8-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 360 CV
Weight:
8Do: 450 CV.

"Nice inverted-V Potez engine"
Model: 9-Ab, -A
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 250 CV @ 2700 rpm
Weight:

"Potez 9A"
Model: 9-B, -Ba, -Bb
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 220 CV @ 2400 rpm
Weight:

"Potez, 9B"
Model: 9-C
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 220 CV @ 2500 rpm
Weight:

"Potez 9C-01"
Model: 9-E
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 225 CV @ rpm
Weight:

"Potez 9E"
Model: Coroller (A-4)
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 50 CV
Weight:
Vertically in-line

"Potez engine on VIII aircraft from 1920"
Model: Potez-Farman
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Potez-Rateau
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:


