Updated: 27-Aug-2020
With roots in the Tsarist era, 30 hp, 4-cylinder Wright-type engines were built in Riga with Kalep as director (see).
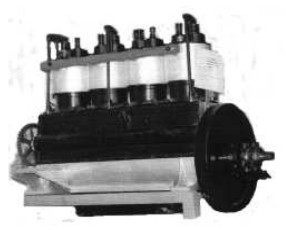
“Wright de Motor”
-The Kalep 80 was an improved version of the Gnome Lambda. First, they directly bought the license for the Omega, which they did not build, but they did make a derivative of this engine.
Gnomes of 60, 80 and 100 CV were also made. During the First World War the "Motor" factory moved from Riga to Moscow and was headed by A.D. Shvetsov (see), who would later become a great designer.
-They started making the LeRhone Jb. At the end of this engine series, in 1917, the factory closed.
-But the Moscow Motor (GAZ number 4) kept a small OKB that collaborated in the development of engines from other factories.
-It is said that they made the R.A.M. engines, contraction of Russkiy Aviatsionniy Motor, of greater power like the M-8, with projects that lasted until 1928.
-They have also participated in the M-11 design but under a denomination M-100 that has nothing to do with the V-12.
-GAZ 4 later became GAZ 24. -This seems constant, the change factory and engine names. (see Shvetsov -m-25 engine, etc-).
-It is assumed that today it is the "-300", although at the beginning of 1955 it was mentioned as Motor GNPP/GAZ number 26.
-In that year 1955 it was already involved in the evolution of Mikulin's RD-9, later Soyuz.
-They were more fully involved with the R-11K (today Soyuz R-11-300).
-Sergei Gavrilov took over in 1962, initially dedicating himself to improving the R-11 from which the R-13 was derived, which was ready in 1966.

“R-13”
-The R-13 in its different versions delivered an average thrust of 9,000 lbf dry, and 14,000 lbf with afterburner.
-The Motor-R-25 engine was a new design. Due to its dimensions it was capable of replacing other engines on airplanes that received a new life in this way.
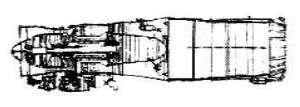
“Motor R-25”
-The R-25 engines went to modernize the MiG-21 and Su-15. These engines have also been manufactured by HAL in India for their own aircraft.
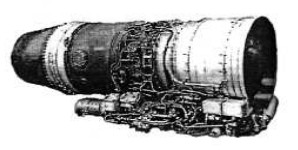
“R-95”
-The R-95 began to be developed in 1975 for the next generation of aircraft, such as the Su-25. They started to build them in 1980.
-It is a twin shaft turbojet that gave 9,000 lbf of dry thrust. The design is done by Gavrilov's team.
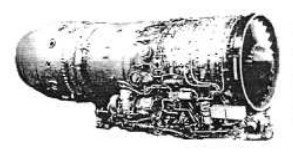
“R-195”
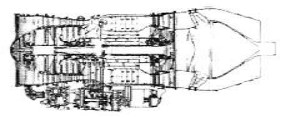
“R-195 schematic drawing”
-Both the R-95 and the R-195 had to have a great survivability in case they were fired at from the ground with the ability to resist 20/23 mm ammunition.
-They delivered almost 9,500 lbf of thrust, and were intended for the latest versions of the Su-25, Su-28 and Su-29.
Engines of MOTOR
Model: Gnome 100 HP (Lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Gnome 60 HP (Lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Gnome 80 HP (Lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: LeRhone 9Jb, (Lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: M-8
Model: R-11
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:
Model: R-13
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:

"Motor R-13"
Model: R-195
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:

"Motor R-195"
Model: R-25
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:

"Motor R-25"
Model: R-95
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:

"Motor R-95"
Model: Wright, 4 cyl, 30 HP (Lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:

"Motor Wright"


