Updated: 15-Jun-2020
In 1909 Wilhelm Maybach left Daimler where he was Chief Designer to found his own company, Maybach Motorenbau GmBH.
-It was a subsidiary company of Count Zeppelin, manufacturer of the famous airships.

“Maybach Motorenbau logos”
-On the other hand, first, together with his son he had founded the "Luftfahrzeug-Motorenbau-GmBH" in Bissengen in 1909.
-They moved to Friedrichshafen next to the Zeppelin factory, after three years entering the Count's orbit and changing the name to the definitive "Maybach Motorenbau".
-Maybach went on to produce engines for actually all German airships, especially Zeppelin and Schütte-Lanz.
-In the same year 1909, the AZ, 130 Kw motor was already mounted on the LZ-9, LZ-10 and LZ-12 Zeppelins.
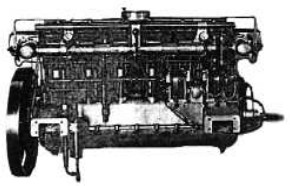
“Motor AZ”
-Of the same 6-cylinder in-line engine with double ignition a front cross-section is shown below.
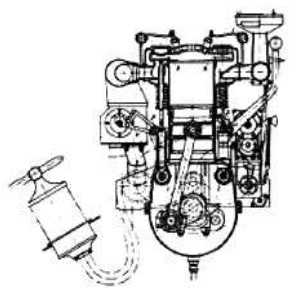
“Maybach AZ cross-section”
-The AZ motor was also built by Italian Itala and one of these engines is found at the Polito de Torino.

“Maybach-Itala AZ”
-Of course, the Maybach chapter offers the range of aviation engines built by the German brand. We do not mention their marine and armored tank engines.
-Chronologically the Maybach CX that gave 145 CV at 1,100 rpm was from the year 1910. It had 6 cylinders in line. The 6-cylinder in-line CX that gave 180 CV at 1,200 rpm came out towards 1913.
The 6-cylinder in-line CX that gave 210 CV at 1,250 rpm appeared in 1914.
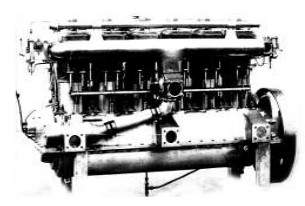
“Maybach CX”
-The Maybach CX engines were used on airships as from the year 1911. The last ones to carry it were the LZ-93 and the SL-8.
-In general they used Maybach carburetors and Bosch magnetos.
-They were also used in some aircraft such as the Zeppelin-Staaken, models VG I and II (in addition to the L-40 and L-56 airships), which was the case of the Maybach HSD engine, from the year 1915.
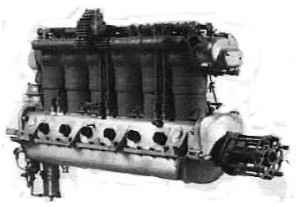
“Maybach HSD”
-The shown photograph of the HSD model is obtained at the Polytechnic of Turin, where it is deposited.
-Another similar engine was the MbIVa giving 235 CV at 1,600 rpm. It was installed on the Staaken R-XIV for example.
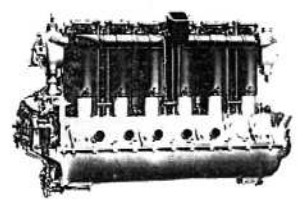
“Maybach MbIVa”
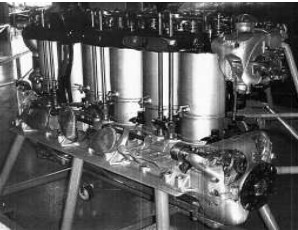
"MbIVa, at the MAE in Paris"
-In 1919, the 240 CV engine was upgraded and it already had aluminum cylinder heads and increased bores, so it reached 260 CV. It was mounted on the "Bodensee" airship.
-The HSLu model engine gave 240 CV and was first installed on the L-15 airship in 1915.
-On the Zeppelins type P and Q, four of these engines were installed, ending up with six.
-Later the 300 CV engine was derived from the 240 CV.
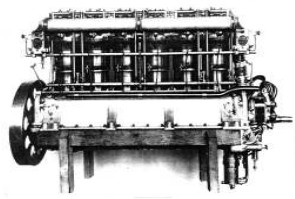
“Maybach HSLu”
-The 300 CV from 1918 still had six cylinders in line. We see below two photographs on both sides.
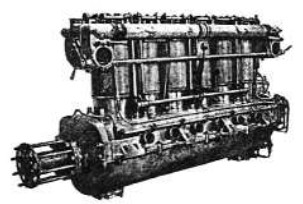
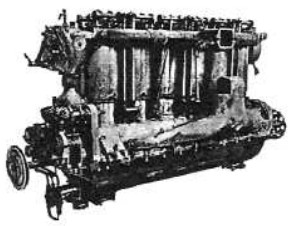
“Maybach, 300 CV”
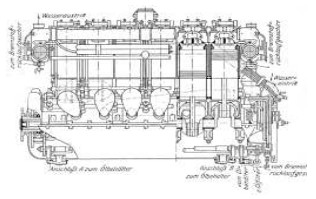
-And the same motor in side and front cross-section views.
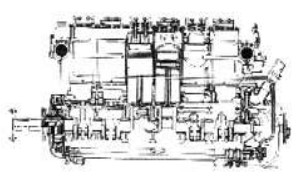
“Maybach 300 CV engine cross-sections”
-We can see the construction details in the previous cuts. The double camshaft stands out, one for exhaust and the other for intake.
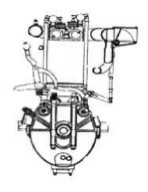
Below we show a photography of a Maybach six-cylinder, giving 300 CV at 1,500 rpm, installed on an airplane.
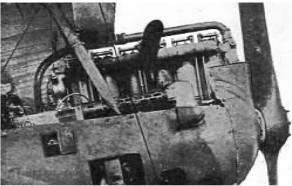
“Maybach engine installation”
-Below we provide the 180 CV, 210 CV, 245 CV and 420 CV Maybach engines.
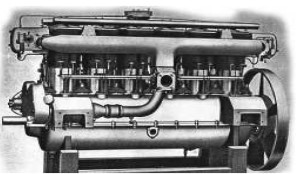
“Maybach, 180 CV”
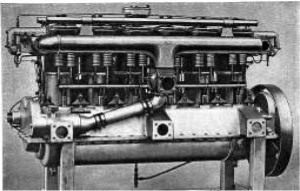
“Maybach 210 CV”
“Maybach 245 CV”
-We get information from Maybach regarding the GO series, high speed and Diesel. The GO-4 was a six-cylinder that gave 150 CV at 1,400 rpm. The GO-56 was the V-12 version of the previous one with two of its six-cylinder blocks. It delivered 410 CV at 1,400 rpm, and was designed for airships.
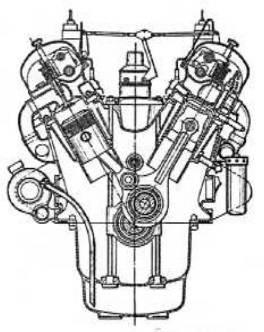
“Maybach GO-56”
-Very beautiful the master rod with its connection to the connecting rod. The engine had ball and roller bearings.
-After WWI and because of the Treaty of Versailles, Maybach started to manufacture automobiles achieving popularity.
-After the lapse, in 1924 they returned to the manufacturing of engines for the airships that were rebuilt at that time.

“Zeppelin airship”
-So in 1926, the "Norge" is powered by three 245 CV Maybachs.
-The "Italia" had three 250 CV Maybachs in 1928.
-In these years the 12V with 400 CV appears. The famous American "Los Angeles" carried five of these Maybach engines on outside platforms. It was the ex-German LZ-126 and had a reverse drive and direct propeller drive.
-The Maybach model VL-2 delivered 530/570 CV. They were mounted on the LZ-127 and LZ-129.
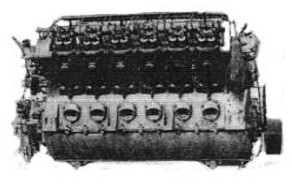
“Maybach V-12”
-The 1928 LZ-127 "Graf Zeppelin" was powered by 5 engines of the 530 CV version.
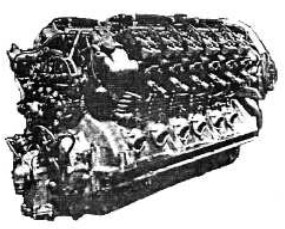
“VL-2 530 CV”
-Also for the first time a gaseous fuel called “Blaugas” was used. It had a density equal to that of air.
-Maybach engines powered many German submarines, U-Boats.
-Lately we received two photographs of the Maybach VL-1 400/420 CV, VL-1 models.

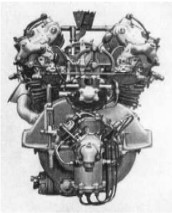
“Two views of the Maybach 400/420 CV”
From Appendix A6: Below a clearer view of a Maybach that was used in WWI on German bomber planes.

-And now, located on Flickr / Photos, a Maybach GO4 Diesel that is mentioned in the main text.

“Maybach GO4” (PiP)
-We received curious photos from the moment of the installation of a Maybach VL-2 on the Graf Zeppelin.
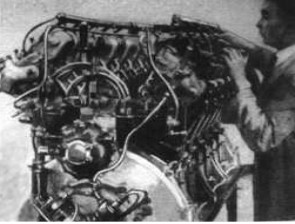
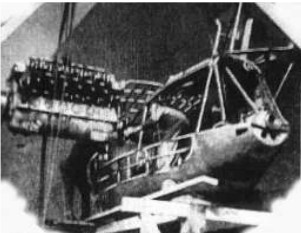

“Preparación, instalación y ajustes finales”
From Appendix 9: The Mb-VII airship engine, here on display at the Friedrichshafen museum, delivers 520 CV. They are twelve cylinders in "U".
-In fact it is a motor resulting from coupling two Mb-IV side by side with a front gearbox for coupling and reduction. They were built between 1910 and 1918.

"The Mb-VII, in fact a Twin Mb-IV"
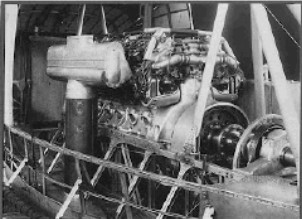
“Installation of a Maybach in an engine car”
-Maybach Motorenbau, adapted many of its engines for the different airships of the First World War.
-The following photo belongs to another example.
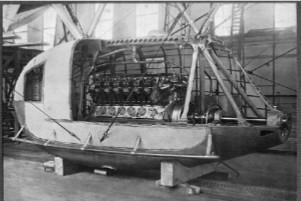
“Engine car in installation process”
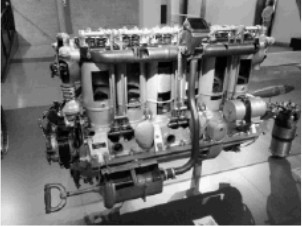
“Mb-IV with suction primer”

“Friedrichshafen engine hall”
-Engine seen in Japan that was installed on an airship in that country. It is a Maybach model HSLu engine from the year 1915.


“Two views of the Maybach HSLu”
From Appendix 10: In a virtual discussion in a forum (The Aerodrome) next to a photograph appears a list of engines of this brand and also the Mb-VII.
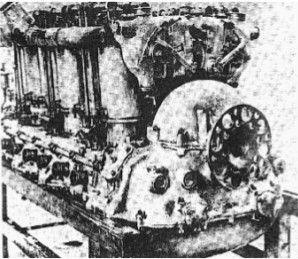
“Maybach Mb-VII”
-The Mb-VII was a 12 cylinder, but NOT in V. It delivered 500 CV at 1,800 rpm. It is an engine with two crankshafts, in fact they are two Mb-IVa joined by a single reduction gearbox.
-The following engines and data are also mentioned, (in addition to those mentioned in the main text):
-Type DW
-Type Mb.III
-Type Mb.IV
-Type Mb.VI
-Type Mb.VII
-The 6 cylinder from 1909 with 140 CV
-The 6-cylinder from 1912 with 165 CV
-The 6-cylinder from 1913 with 180 CV
-The 6-cylinder from 1914 with 210 CV
-The Maybach IR and Mb.III are considered 160 CV.
-The 6-cylinder HS had its derivatives HSD, HSLu, these already gave 240 CV.
-The 240 CV Mb.IVa was produced between 1917 and 1919, along with the other models (in total Maybach made 91123 engines in this period of war).
-Photo of the Maybach 12-cylinder Vee-engine, model VL-2.
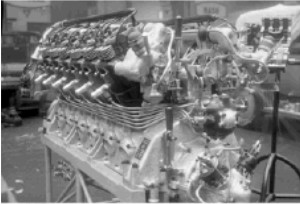
“VL.2, 530/570 CV”
-They were installed on the LZ-127 and LZ-129 Zeppelins.
From Appendix 12: Engine of this brand on a Caspar aircraft under construction.
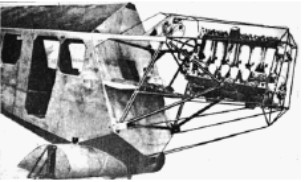
"Possibly a MbIVa" (PiP-Flu)
Engines of MAYBACH
Model: AZ, 140 HP
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 140 CV
Weight:

"Maybach AZ"
Model: CX, 210 HP
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 210 CV @ 1250 rpm
Weight:
CX from 1910: 145 CV at 1100 rpm
CX from 1913: 180 CV at 1200 rpm
CX from 1914: 210 CV at 1250 rpm

"Maybach CX"
Model: DW, 160 HP
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: GO-4
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 150 CV @ 1400 rpm
Weight:
Model: GO-56
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder V-Engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 410 CV @ 1400 rpm
Weight:

"Maybach GO-56, cross-section"
Model: HS, 240 HP
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: HS.Lu, 240 HP (HSLu)
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 240 CV
Weight:

"Maybach HSLu"
Model: HSD
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"Maybach HSD"
Model: Mb.III (IR)
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 160 CV
Weight:
Model: Mb.IV (HS)
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 255 CV
Weight:

"Maybach Mb-IV with starter"
Model: Mb.IVa
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 235 CV @ 1600 rpm
Weight:

"Maybach MbIVa, at the MAE in Paris"
Model: Mb.VII
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder U-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 500 CV @ 1800 rpm
Weight:

"Maybach Mb-VII, actually a Twin Mb-IV"
Model: VG.1o
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: VL.1
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder V-Engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 420 CV
Weight:

"Maybach 400/420 CV, side view"
Model: VL.2
Arquitecture: V-Engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 570 CV
Weight:

"Maybach VL-2, 530 CV"


