Updated: 04-Apr-2019
Hellmuth Hirth and his brother Dr. Ernst Hirth developed and manufactured excellent engines with outstanding features.
-The father of both, Albert, was already related as a remarkable engineer in tool design together with his brother Wolfram-Wolf-Hirth, who was a famous glider designer and pilot.

“Hellmuth Hirth”
-Although the HM-60 has always been mentioned as the first Hirth engine, an earlier one has been located in an old book. It is considered one of the first engines, and it had three upright inline cylinders. It was water-cooled and was installed on the small Darmstadt "Mahomet" plane.
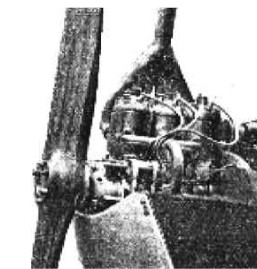
“Hirth on the Mahomet”
-As we have already seen in Heinkel's chapter, Hellmuth lost his life in an aviation accident in July 1938, and his brother Ernst continued until 1941. The company was acquired by the well-known aircraft manufacturing brand, becoming known as Heinkel-Hirth. This company continued its trajectory until the end of WWII, adding its turbine projects.
-Later, it resurrected for small snowmobile engines, etc. and eventually it was acquired by Göbler (see Göbler-Hirth).
-In 1923, the 65 CV HM-60 was already produced.
-Its most indicated points were the use of roller bearings both in the crankshaft and in the crankpins.
-To do this, the crankshaft was divided into multiple pieces with an exact adjustment between them. It had a wonderful mechanization system, worthy of seeing in detail.

“Part of the Hirth crankshaft”
-With a magnificent mechanical construction.
-Greasing was done by small jets of oil directed towards each bearing, resulting in a great rotation lightness.
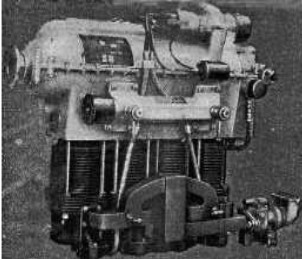
“HM-60”
We can see the loop made by the intake manifold and the position of the carburetor, behind the engine and with horizontal draft.
-In 1927, this engine had already won several contests. Finally in 1931 "Hirth Motoren GmBH" was founded.
-A Hirth HM-60 version was the HM-60R with 80 CV.

“Hirth HM60R”
-From that moment the brand's best known engines are produced, those of the series "500": the HM-504, HM-506, HM-508 and HM-512.
-In between there would be others such as the HM-500, HM-500A of 1938.

“HM-500”

“Hirth, HM-504A”
-At the MAE and in their reserve warehouse there is a Hirth 504-2 with a very good look.

“Hirth 504-2”
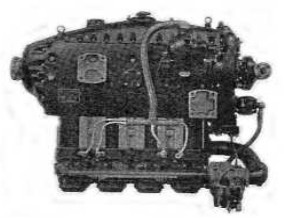
“Hirth 504 A-2”
-The 6-cylinder version was the HM-506. This inverted inline engine gave 150 CV, and its general layout was similar to the previous 4-cylinder series.
-They were installed on the Spanish INTA HM-5 aircraft.
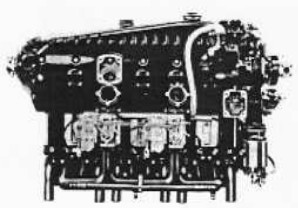
“Hirth, HM-506A”
-The HM-506A in the illustration below gave 160 CV at 2,500 rpm, and is an improvement of the previous one, the HM-506.
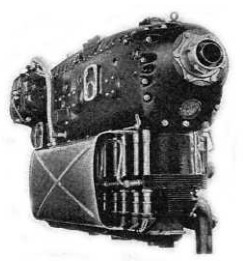
“Another view of the HM-506 A”
-The HM-508 already had 8 cylinders in inverted V configuration, really nice looking. The power was 280 CV.

“Hirth, HM-508”
-The HM-508D-1 that gave 280 CV, was mechanically supercharged, as we can see from the rear.
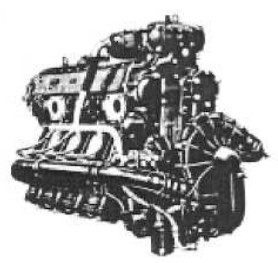
“Hirth, HM-508D-1”
-There were versions like the HM-508F with 220 CV, the HM-508J with 240 CV, the HM-508C with 270 CV, HM-508E with 240 CV, etc.
-The HM-512 had 12 cylinders in inverted V configuration and gave 400 CV. It was mounted on the "Taifun" and Messerschmitt Me-108-C, for example.

“HM-512”
-The HM-512 had two versions, the A with 400 CV at 3,110 rpm and the B with 450 CV at 3,100 rpm.
-The power for A is at sea level and B's is at an altitude of 3,000 meters. (9843 ft)
-The HM-512s were inverted V12 engines with the cylinder banks at 60°. They were geared and supercharged. Below, we see the -A version.
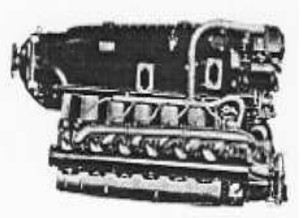
“HM-512A”
-The Taifun Me-108 series A and B-0 used the HM-8U Vee-engines that were derived from the 8-cylinder, inverted-V HM-60 engine with the same cylinders.
-With gearbox, they gave 240 CV at 3,000 rpm.
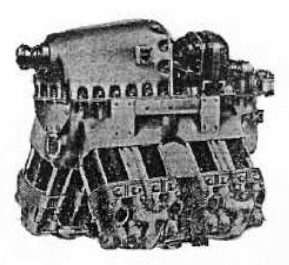
“Hirth, HM-150”
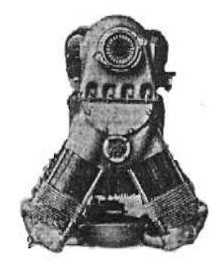
“HM-150, front view”
-Having looked at these most common engines, now we present a very unknown one, the HM-150, which is a very remarkable in design. We show it in three views.
-It gave 220 CV with a weight of 165 Kgs.
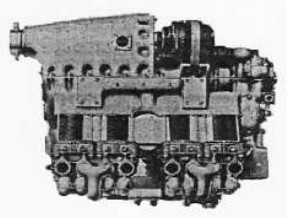
“Hirth, HM-150”
-The HM-150, with its characteristic block and gearbox, and its cylinders in V in a clearer view.

“HM-150”
-It started with 170 CV at 2,250 rpm and was increasing up to 215 CV at 3,000 rpm with the HM-150U.
From Appendix 6: In October 1934 Hirth announces an eight-cylinder inverted Vee-engine, model HM8U. Possibly with reference HM-508U.
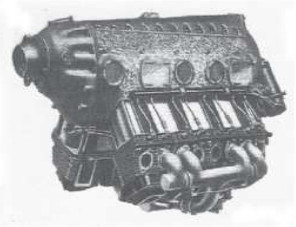
“HM-8U”
-Hirth was reborn over time as Göbler-Hirth. The product range in 2011, according to its catalog is the following:
-First there is an industrial line, in the range of small electric generators or transfer pumps, etc.
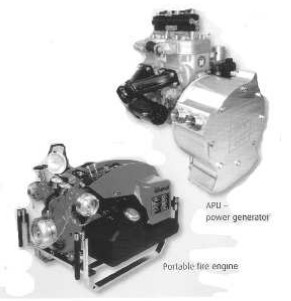
“Two Göbler-Hirth industrial products”







-We showed the main lines of G-H engines with the series being headings of a group: for example Series 32 gives cause to 3203 and others.
-The majority is for aeronautical use although also for marine and terrestrial.
-As we are dealing with the aeronautical issue here, Göbler-Hirth engines are well known for their proliferation.
-This is why new engines are being developed like the most powerful one that we can see in CAD drawing below.

“CAD design”
-There are new applications in UAV aircraft, for mainly military uses. The brand has had the talent in orienting itself towards this field.

"The vehicle and its engine"

“Another example”

“And another”
From Appendix 9: In the Koprivnice Museum there is a Hirth 504-A2 in good condition. Photo taken by E-V of AEHS.
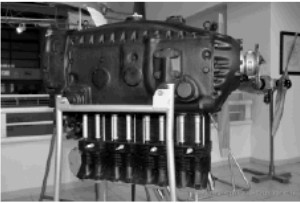
“Hirth 504-A2 on a stand”

"In the absence of magnetos"

“Engine plate details”
-At the Laatzen Museum, a Hirth 500 is exhibited. This small 4-cylinder has an unbeatable look.

“Right side view” (E-V)

“Rear view” (E-V)
-What calls our attention, is the density of accessories in this part.
-At the Vienna Aviation Museum, there are several engines exposed, including a cutaway Hirth HR-60R showing the beautifully machined and polished internal parts. This unique brand of engines has a design based on ball bearings and rollers in all moving parts.

“Hirth HR-60R” (E-V)
-The crank heads are closed, instead of split as it is the case with those that use antifriction bearings, to accommodate the entire roller bearings.
-This has the consequence that the crankshaft must be divided into several parts in order to carry out the assembly.
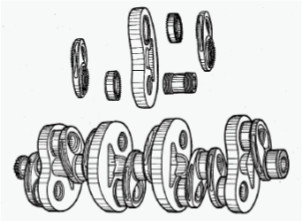
“Hirth crankshaft details”
-Amazing is the accuracy with which all the jagged laces and the firm union between everything must have been mechanized.
-They express the excellence of mechanization of the entire engine, especially the steel ones.
-We must pay attention to the joining parts of the crankshaft, which instead of being a single piece, is made of multiple parts that fit like those of a clock.
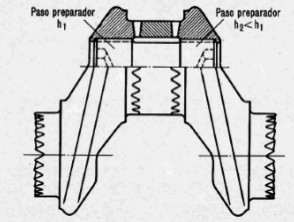
“Mechanical assembly details”
-There is no doubt about the exquisiteness of fitting the parts without misalignments of journals. A bolt with two differential threads connects each main journal with two cranks.
From Appendix 12: News from this brand in 2016: There is the 3703 and an update for the 4103, the 3504-di and the F-23.

“Hirth, 4103”

“Hirth, F-23”

“Hirth, 3703”

“Hirth, 3504 di”
-New series of Hirth engine photographs from the pre-war period, taken from the Flugsport magazine.
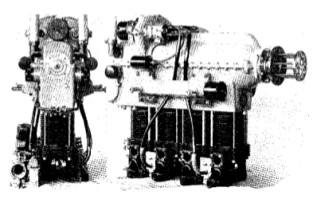
“HM-60, de 65CV”
-Below a triptych of this same engine.
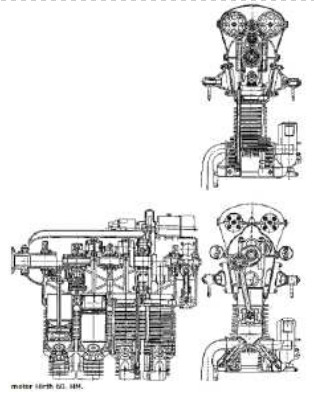
“HM-60 triptych”
-And an ad for the HM60R, with 80 CV.
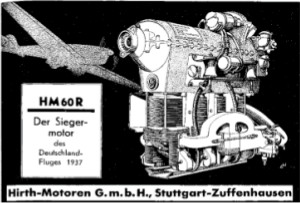
"HM-60-R ad"
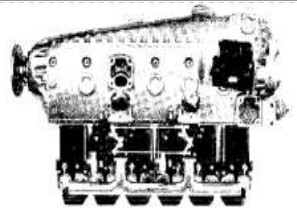
"Hirth HM-506"
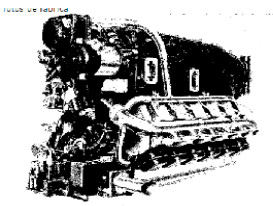
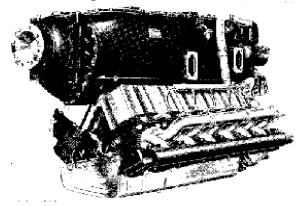
“Hirth HM-512”

“Standard hub for Hirth engines”

“Hirth HM-8A ad”
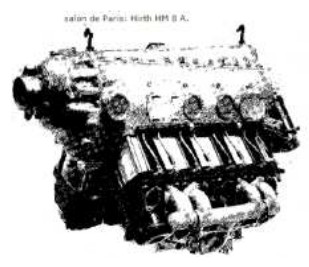
"HM-8A presented at a Paris Salon"
Engines of HIRTH
Model: 2702 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 521 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 52 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 31 Kg
Model: 2703 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 521 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 52 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 31 Kg
Model: 2704 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 53 CV @ 5500 rpm
Weight: 33 Kg
Model: 2706 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 65 CV @ 6200 rpm
Weight:
Model: 3002 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 1042 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 80 CV @ 5500 rpm
Weight: 48 Kg
Model: 3003 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement: 1042 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 100 CV @ 6200 rpm
Weight: 48 Kg
Model: 3202 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 55 CV @ 5500 rpm
Weight: 31 Kg
Model: 3203 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 55 CV @ 5500 rpm
Weight: 31 Kg
Model: 3502 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 70 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 36 Kg
Model: 3503 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 70 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 36 Kg

"Hirth, 3503 HF"
Model: 3504di (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 625 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 60 CV @ 6300 rpm
Weight: 38 Kg

"Hirth, 3504 di"
Model: 3701 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke3-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 939 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 90 CV @ 5200 rpm
Weight: 45 Kg
Model: 3702 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke3-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 939 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 84 HP
Weight:
Model: 3703 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 3-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 939 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 100 CV @ 5500 rpm
Weight: 49 Kg

"Hirth, 3703"
Model: 3801 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"Hirth, 3801"
Model: 4103 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 100 cc
Bore / Stroke: 44 x 37 mm
Power: 8 CV @ 6700 rpm
Weight: 3 Kg

"Hirth, 4103"
Model: 4201
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 183 cc
Bore / Stroke: 54 x 40 mm
Power: 15 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 6 Kg
Model: F-102 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 26 CV
Weight:
Model: F-23 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 521 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 50 HP @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 22 Kg

"Hirth, F23 lightweight"
Model: F-263 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke2-cylinder In-line
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 383 cc
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 30 CV
Weight: 32 Kg
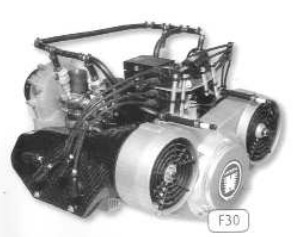
Model: F-30 (3003) (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 1042 cc
Bore / Stroke: 72 x 64 mm
Power: 92 CV @ 6500 rpm
Weight: 42 Kg

"Hirth, F30"
Model: F-31 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: F-33 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke Single-cylinder
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 312 cc
Bore / Stroke: 76 x 69 mm
Power: 25 CV @ 6200 rpm
Weight: 13 Kg

"Hirth, F33"
Model: F-36 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture: 2-stroke Single-cylinder
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 210 cc
Bore / Stroke: 70 x 54 mm
Power: 15 HP @ 6000 rpm
Weight: 13 Kg
Model: Heinkel HeS 8
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s: Centrifugal-axial compressor
Combustion chambers:
Turbines: Single stage turbine
Power / Thrust: --- / 1570 Lbf
Weight: 380 Kg
Model: HeS-011, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s: Diagonal with 3-stage axial
Combustion chambers: 16 chambers
Turbines: 2-stage turbine, axial flow
Power / Thrust: --- / 2866 Lbf
Weight: 950 Kg
Model: HeS-1, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
Model: HeS-3, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s: 14-blade inducer + 16-blade centrifugal compressor
Combustion chambers: Reverse-flow annular combustion chamber
Turbines: 12-blade radial inflow turbine
Power / Thrust: --- / 1100 Lbf
Weight: 360 Kg
Model: HeS-30, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s: 5 axial stages
Combustion chambers: 10 cannular combustion chambers
Turbines: 1 axial stage
Power / Thrust: --- / 1896 Lbf
Weight: 390 Kg
Model: HeS-40, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
Model: HeS-50, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
Model: HeS-60, Heinkel-Hirth
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Hirth F-10 (ver Göbler-Hirth)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: HM-150, -U
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:

"Hirth, HM-150"
Model: HM-500, -500A
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 3983 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115
Power: 105 HP @ 2500 rpm
Weight: 92 Kg

"Hirth, 500 at the Laatzen Museum"
Model: HM-501
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 5970 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115 mm
Power: 160 CV @ 2380 rpm
Weight: 148 Kg
Model: HM-504, -504A, -504A2
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 3998 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115 mm
Power: 105 CV @ 2500 rpm
Weight: 107 Kg

"Hirth, HM-504A"
Model: HM-506, -506A
Arquitecture: 6-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling:
Total Displacement: 5980 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115 mm
Power: 160 CV @ 2500 rpm
Weight:

"Hirth, HM-506A"
Model: HM-508, V(inv.)
Arquitecture: 8-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 7970 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115 mm
Power: 280 CV @ 3000 rpm
Weight: 208 Kg

"Hirth, HM-508"
Model: HM-512, -A, -B
Arquitecture: 4-stroke12-cylinder Inverted V-engine
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 11940 cc
Bore / Stroke: 105 x 115 mm
Power: 400 CV @ 3110 rpm
Weight: 270 Kg

"Hirth, HM-512"
Model: HM-515
Arquitecture: 4-stroke4-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 2980 cc
Bore / Stroke: 95 x 105 mm
Power: 65 CV @ 2100 rpm
Weight: 74 Kg
Model: HM-60, -60R
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder In line inverted
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement: 3600 cc
Bore / Stroke: 102 x 110 mm
Power: 65 CV @ 2400 rpm
Weight:

"Hirth HM-60"
Model: HM-8, -A,-U, -V
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:

"Hirth, HM-8U"


