Updated: 03-Jan-2019
See EMG. Eugene M. Gluhareff was a pioneer in ultralight helicopters.
-His engines were installed on the the rotor tips.
-By 1955 he tested the first engine model, the G8-2.
-They could also propel glider planes
-The G8-2 was unprecedented, with continuous combustion. First the fuel was vaporized, and in this form it entered the combustion chamber. Resonance was not desirable so the nozzle was modified in the shape of a fish.

“Gluhareff G8-2-”
-It was designed by Eugene H. Gluhareff, in the first illustration of an advertisement we see the sectioned engine and the vaporizer inside.

“Gluhareff advertisement”
-On the leading edge of the blade that is hold by a person, we see three air intakes, one in the notch near the left hand. The other two are further back -near the right hand- at the front and in another major notch. All inlets have a slight trumpet shape.
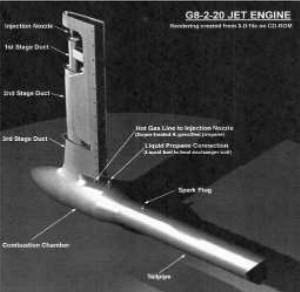
“Gluhareff G8-2-20”
-Finally, Eugene himself holds a 130 lbs type pressure reactor, as they are called.

“Gluhareff holding the 130 lbs pressure reactor”
-This is the G2-8-130 model. We clearly appreciate the two notches at the front of the blade, with the three air inlets.
-There is no direct frontal intake to the camera itself, which is streamlined and we can see the "fish tail" cut on the exit nozzle.
From Appendix 6: Licensed Aeronautical Engineer Eugene Gluhareff, was born in St. Petersburg, Russia and emigrated to the US in the 1920s.
-He was an employee at Sikorsky where he worked closely with both Igor I. and Igor A. Sikorsky.
-But Gluhareff is best known for developing a valveless pulsorreactor (see main text and annexes).
-He made several models with different sizes and powers, but from what has been seen later, the G8-2 model has been the best solved and most used.

“Gluhareff G8-2 on EMG-300 helicopter”
-These engines were used in several small helicopters and artifacts such as the MEG-3X of the Gluhareff himself, towards the 1960's.
-The pilot was standing on top of the device.

“The Gluhareff MEG-3X”
-On the Gluhareff MEG-1X and 2X, the rotor is above the pilot's head.
-The engines are still the G8-2. (MEG = EMG)

“The MEG-2X”
-Four years before he had already tried the MEG-1X, which was clearly simpler.
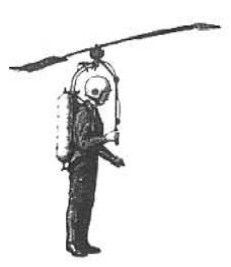
“The MEG-1X”
-The most common G8-2 engines were the G8-2-20, G8-2-40, G8-2-80 and G8-2-130.
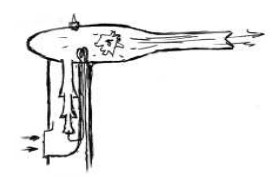
"Multiple intake venturis and fuel heater"

“A Gluhareff in the dark”
Engines of GLUHAREFF
Model: G8-2 series
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:

"Gluhareff G8-2"
Model: G8-2-130
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:

"Gluhareff holding the 130 lbs. engine"
Model: G8-2-15
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: G8-2-20
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:

"G8-2-20 illustration"
Model: G8-2-250
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: G8-2-40
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: G8-2-80
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:


