Updated: 01-Aug-2018
Around 1927, Engineer Causan developed an incredible engine composed of four V-engines attached by their heads, using common combustion chambers.
"Etchegoin-Causan schematic diagram"
-Admission was made at one base of the cylinder and the exhaust at the opposite base.
-It used a 2-stroke cycle, but it had to be "blown" in order to make an efficient sweep. For this it had a mechanical supercharger.
-Foreseen for 700 hp at 2,400 rpm. There is no known application.
From Appendix 7: Dr. Etchegoin was a doctor specialized in tuberculosis issues at the Pasteur Institute, and closely related to the engineer Causan. Both came up with the idea for an opposed piston engine that had many derivatives by Mr. Causan himself.

“Etchagoin and Causan” (P¡P)
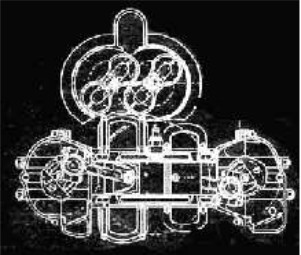
“Engine diagram” (PiP)
-The collaboration between the two men emerged ideas like this automotive engine that later would give rise to the famous Junkers 223 and 224.
-The principle of opposite pistons with crankshafts at the ends we would see in the Junkers 203, 204, 205.
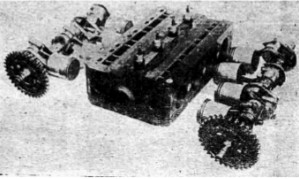
"Central block and crankshafts"
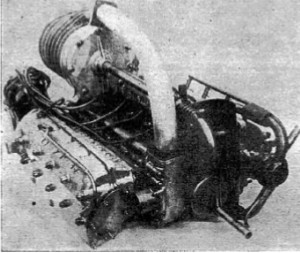
"Another view of the engine with its Roots supercharger"
-It used a two-stroke cycle and had a mechanical Roots supercharger that we can see perfectly in the drawing of the sectioned engine.
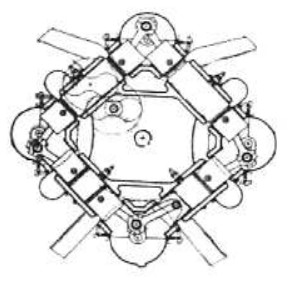
-Using the same opposite-piston principle, Causan himself made a more complex engine, but analyzing it, it was made from four V-engines joined by their cylinder heads.
-The four crankshafts had gears, in which there must be flywheels, that engaged in a larger gear that coordinates the shafts, and at the same time supplying the power output towards the propeller shaft.
-This we see clearly in the schematic diagram below. We can imagine the four V-engines and it is also clear that it is a 2-stroke engine.
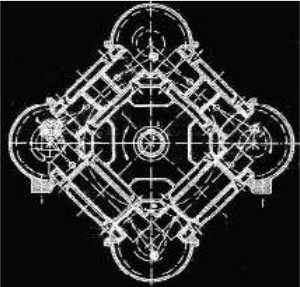
"Causan's diagram derived from Etchegoin-Causan" (PiP-ANC)
-The information in this chapter is due to the Association of Friends of Nemorin-Laurent Causan.
Del Apéndice 10: Diseñador de motores originales. Ver el texto principal.
From Appendix 10: Original engine designer. See the main text
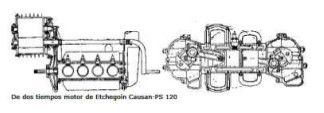
“Two-stroke, opposite-piston engine”
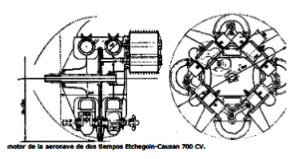
"More complex system than the previous one"
-In each cylinder there are two pistons connected to opposite crankshafts. Each cylinder has two pistons working with the two-stroke cycle. The ports are at the end of the strokes.
Engines of ETCHEGOIN - CAUSAN
Model: Motores complejos, pistones opuestos y 2T
Arquitecture: Opposed piston engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:


