Updated: 21-Feb-2025
TALLERES NACIONALES DE CONSTRUCCIONES AERONAUTICAS
(Mexico)
TALLERES NACIONALES DE CONSTRUCCIONES AERONAUTICAS engine specifications
This company was also known as TNCA and was founded in 1915.
-The truth is that since the first years of motorized aviation they already built aeronautical material such as airplanes, engines and propellers.
-In their revolutionary civil war they already used French and American airplanes.
-They acquired licenses to build them and soon Mexican airplanes appeared such as the Series A and H.
-The first engine licenses were from Anzani, Gnome e Hispano-Suiza, (and the 180 HP BMW).
-The airplanes built at TNCA intervened in the Mexican civil war.

“TNCA Series H airplane with an Aztatl engine”
-The Serie C airplanes were powered by the 150 HP Hispano Suiza like the engine that is still exhibited at the FAM Museum.
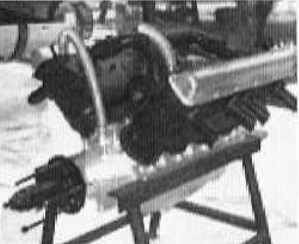
“Hispano-Suiza engine at the FAM Museum”
-The first three engines built were:
-The “Trébol” licensed by the Anzani with 3 cylinders and 45 HP.
-The “Aztatl” from 1917 was the Anzani with 6 cylinders and 80 HP. By the way, the name Aztatl comes from “Garza Blanca” in Nahuatl.
-Here we have a doubt because it is stated in a publication that the Garza Blanca was an original Mexican design from 1916 and with the pistons on the outside (?).
-Insistent clarification “Garza Blanca” is “Aztatl” in Nahuatl.
-In 1916 the Barcelona brand Hispano-Suiza (see) created the SS México in Mexico to introduce its engines.
-Another Mexican design was the 10-cylinder, 110 HP engine, but its origin or lineage is not confirmed. The search is still ongoing, although other references only give it as a national design.
This is the manufacturing center called Talleres Nacionales de Construcciones Aeronauticas, also known as TNCA.
-In 1917 the first aeronautical engine in Mexico was made: the Aztatl (see), a fixed radial under license from Anzani.
-The three-cylinder, 45 HP engines, called the Trebol, was made by this brand. The six-cylinder engine was the Aztatl that gave 80 HP.
-The ten-cylinder, 110 HP engine was known as the SS Mexico.
From Appendix 9: The SEA radial engine that we present is a novelty sent from a Mexican collaborator of the SMEAL company. It is a design by engineer Sea, built by Talleres Nacionales de Construcciones Aeronauticas. Photo Tohtli, via Oscar F.R. Alvarado.

“5 cylinders and 125 HP”
-National Workshops of Aeronautical Constructions. Through both the Historical Society of Aeronautics of Mexico (SMEAL) and the Tohtli publication, they have recovered information on the manufactured materials. Especially aircraft engines.
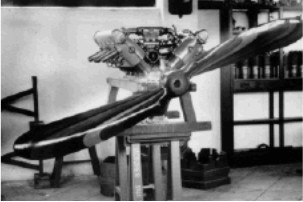
“Hispano-Suiza engine with Anahuac propeller”
-Attention to detail: This engine still has cooling fins under the cylinder water blocks. Therefore it is one of those purchased along with the documentation and tools from Hispano-Suiza in Barcelona to build them under license in Mexico. They were intended for TNCA C series aircraft.
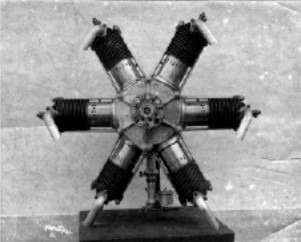
“6-cylinder Aztatl indigenous engine”
-In Mexico, the Aztatl engine is considered the first national aviation engine manufactured and designed in that country.
-The central block features the cast letters “Aztatl-Mexico” and “TNCA”. According to known history, the TNCA had acquired licenses to build engines.
-Among them are the 6-cylinder Anzani. The Aztatl, in the author's opinion, is totally “inspired” by the 6-cylinder Anzani (as the SS Mexico is by the 10-cylinder).
-Without undermining or disparaging the merit of the execution of these engines, knowing the difficulties of the time, it is a work of a very high technical level.
-The most notable differences may be in the exhaust outlets: In the Anzani they are forked in a “Y” and in the “Aztatl” they are bent and directed downwards.
-Another report: The Aztatl engine was the first aviation engine built and designed in Mexico. It was a 6-cylinder, 80-horsepower engine. Its construction began in February 1917 under the direction of Alberto Salinas Carranza and with the cooperation of Francisco Santarini, who, taking into account the needs of the Military Aviation School and the resources available, designed an airplane engine capable of soaring in the altitudes of Mexico. Tothli February 1919.
-The Salinas Carranza archive provides information on the constitutionalism movement and the beginnings of aviation in Mexico.
-General Alberto Salinas Carranza, nephew of Venustiano Carranza, was born in Coahuila in 1892. He was sent by the Mexican government to study aviation in the United States in 1912.
-TNCA National Workshops for Aeronautical Construction.
-Other Description: The Aztatl engine was the first aeronautical engine made in Mexico and dates back to 1917. The design was a six-cylinder, air-cooled, fixed radial type.
-Other engines were built in three (45 hp), six (80 hp), and ten-cylinder (110 hp) versions.1 The ten-cylinder engine was called the SS Mexico and the three-cylinder, 45 hp engine was called the Trébol.
-The Anzani, Gnome, and Hispano Suiza were also rebuilt under license, and some aircraft were fitted with a 60 hp Wright engine and others with a Renault.
-TNCA Series C - Biplane, this one was powered by a Hispano-Suiza engine. This aircraft was also called Microplane Veloz or Microbio.

“Mechanics and pilots in front of an Aztatl”
-We can clearly see the angled exhaust pipes directed towards the ground.
-Unlike the below photograph from the A. Salinas Archive, where the engine at the back has the exhaust pipes of the Anzani engines.

“Personalities of the Mexican aviation in front of an Anzani”
-Another example of the existence of Anzani engines (original or manufactured in Mexico) is the following one on a test stand at the TNCA factory.
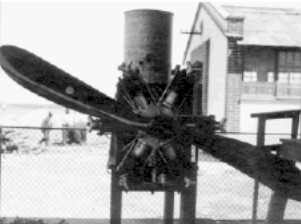
“Anzani with Anahuac propeller”
-The Author emphasizes the detail that in the place where the “Aztatl” engine has the indication “TNCA”, the original French Anzani has the inscription “Bte. SGDG” (Breveté: Sanas garantie du Government) or (Patented, without Government guarantee)
From Appendix 12: The company is Talleres Nacionales de Construcciones Aeronáuticas. The Trébol was the three-cylinder engine of which we have obtained two new illustrations.
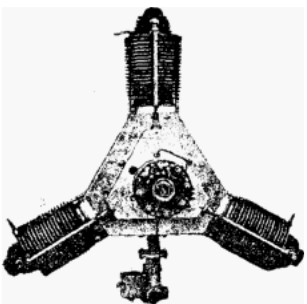
“The three-cylinder Trébol”
-It cannot be said that it is a copy or derivative of the Anzani, since at that time -1920- there were already several brands that used this architecture. The truth is that the central block is very original, triangular.

“Military plane with Trébol engine, in 1920”
-The engine and the aircraft were TNCA products
Engines of TALLERES NACIONALES DE CONSTRUCCIONES AERONAUTICAS
Model: Antoinette and Renault
Model: Azatl, 10 cyl.
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Azatl, 3 cyl.
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Aztatl (Anzani 6 cyl. 80 cv, lic)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Gnome (lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Hispano Suiza (lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Renault (lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: SS México, 10 cyl. 150 hp
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: Trébol (Anzani, 3 cyl. 45 cv, lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: Wright (lic.)
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:


