Updated: 13-Sep-2021
RCV makes a small four-stroke engine with two horizontal cylinders and an innovative device since instead of valves it has ports and a rotating sleeve that with a single port coincides with the cylinder ports in its rotation.
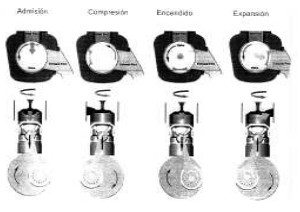
“RCV system principles”
-As we see below, the rotating sleeve has a peripheral gear for its movement.
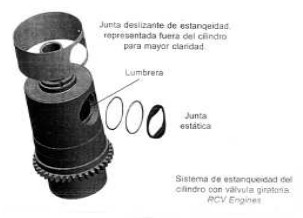
“Sleeve with sealing gasket system”
-The port has a gasket system that does not require the tightness, adjustments and careful construction of the previous English Bristol engines with sliding liners.
-Another example of an RCV engine with rotating sleeves is the one below, but with the difference that the port is in the cylinder head.
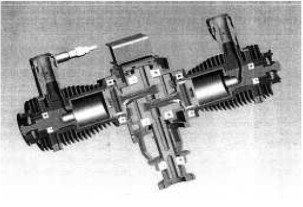
“RCV engine with ports in the cylinder heads”
-RCV engines have been installed on small vertical take-off and landing pilotless vehicles, easily portable in a kind of backpack and capable of carrying day and night cameras, thermal cameras, radio equipment or data transmission cameras, etc.
-It can climb up to 3,000 meters and resist side winds of up to 20 knots.

“Honeywell light vehicle”
-As we can see, the motor is in the center, moving a large fan that produces the lift.
-It has hanging all kinds of sensors that store and send information to the ground. It has inertial and GPS navigation.
- (Extract from the magazine of the Technical Aeronautical Engineers Itavia, from Spain). Knowledge of RCV motors is expanded with more information received from our collaborators.
-The 60 cc boxer is prepared to run on JP5 and JP8 military type kerosene (Heavy Fuel). It is working excellently due to the characteristics of the compact combustion chamber with its high level of generated turbulence. Also by the rotating cylinder.

“RCV engine 60 cc”
-The toothed belts transmit the movement from the crankshaft to the cylinder head that rotates together with the cylinder.
-The ports coincide in their rotation to create the cycles.
-Tests with this type of engine began around 1999, first with single cylinder engines and later with boxers.
-They started with 20cc engines, then 35cc. The first twin-cylinder boxers were the 40 cc that gave 3.4 HP at 9,100 rpm and the 60 cc with 4.6 HP at 8,400 rpm.

“RCV 35 cc engine tests”
They are low power motors but with good performance and reliability, designed exclusively for UAVs, etc.
-Three models stand out in this use (for example, by NWUAV -see-). The RC-70n two-cylinder boxer.

“RCV-70”

“RCV-35”

“El RCV-20, Inline Single Cylinder, axial”

“From an RCV brochure”
From Appendix 11: On the company's website we have found new engines. (August 2021)
-The RCV DF140LC which has 4 horizontally opposed liquid-cooled cylinders with a power of 11.5 hp.

"DF-140LC"
-And the DF70LC with 2 horizontally opposed cylinders giving 5.7 hp at 8,500 rpm. This engine is also liquid cooled.

"DF-70LC"
Engines of RCV Engines Limited
Model: RCV-20, inline
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:
Model: RCV-DF140LC
Arquitecture: 4-stroke4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 140 cc
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 11.5 HP @ 8800 rpm
Weight: 6300 g
Model: RCV-DF35
Arquitecture: 4-stroke Single-cylinder
Cooling:
Total Displacement: 35 cc
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 3 HP @ 8500 rpm
Weight: 2100 g
Air cooled or liquid cooled.

"RCV-35"
Model: RCV-DF70
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"RCV-70"
Model: RCV-DF70LC
Arquitecture: 4-stroke2-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement: 70 cc
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 5.7 HP @ 8500 rpm
Weight: 3000 g
Model: Twin-flat para RPV
Arquitecture:
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke: x
Power:
Weight:


