Updated: 20-Oct-2020
Propulsion Research Center.
The Naval Research Laboratory was located in Chesapeake Beach, MD.
-The team was led by Carroll Porter. Between 1957 and 1958 ran some pulse jets that were similar to the Logan.
-There were tests carried out with devices from 3.5 lbf to more than 20 lbf of thrust
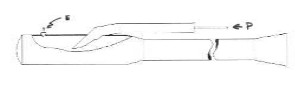
“NRL pulsejet drawing”
-They were valveless pulse jets, as we see the entry of a new fresh charge was directed backwards as in the FWE. This inlet is the one at the top and through “P” the propane inlet, “E” is the starter spark plug.

“NRL pulsejet”
-A 4-inch pulse jet is known to develop 23 lbf of thrust, to install on the ends of rotor blades.
From Appendix 9: A turboshaft to drive on-board generators. It has a heat exchanger based on ceramic honeycombs. Possibly other parts are also made of that material.
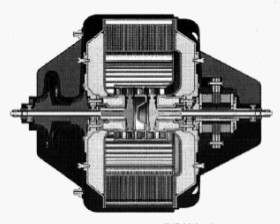
"NRL Turboshaft Engine"
-The gas generator is the shaft on the left. It has two centrifugal compressors in cascade. The exhaust gases pass through the ceramic cells of a heat exchanger that recovers the energy of the gases before going outside.
-This heat is transferred to the air that comes from the compressors. A second turbine -power- drives the shaft on the right.
-It delivers about 4 HP and can drive generators up to 3 kW. NRL also notes that it can be used to power UAVs in addition to APP and APU.
Engines of NAVAL RESEARCH LAB
Model: Ceramic turboshaft
Arquitecture: Turboshaft
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: 4SHP / ---
Weight:

"NRL turboshaft engine"
Model: Pulsejet, 4”
Arquitecture: Pulse jet
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust: 23 Lbf
Weight:


