Updated: 07-Oct-2020
JPL is in NASA's orbit by contract for the study of vehicles and spacecraft, but also the propulsion, which it was initially working on in the 1940s.
-Then it depended on CalTech or California Technical Institute on the basis of Galcit (Guggenheim Aeronautics Lab. of the California Institute of Technology).
-Among the many jobs are rocket propulsion engines, no turbojets nor those that require air for their operation. As an example we show the ones below:

“Ranger spaceship rocket engine”
-The Ranger was used to turn around the Moon and photograph it between 1961 and 1965. Its hydrazine monopropellant engine gave 50 lbf of thrust.
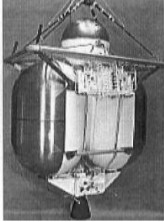
“Viking Orbiter spaceship propulsion engine”
-The Viking Orbiter spacecraft was launched towards Mars in 1975. The engine served to correct the trajectory towards the planet, reduce its speed and place it in orbit of Mars, making constant corrections.
-Therefore it was a multi-starter and delivered about 300 lbf of thrust.
-It had two tanks for fuel and oxidant, one on each side and for feeding it had a spherical tank loaded with helium that pressurized the two main tanks.
Engines of NASA - Jet Propulsion Lab
We have no more detailed engine information for this brand. We continue our search. Any help will be appreciated.


