Updated: 24-Aug-2020
The brothers Louis and Emile Mors, made automobiles since 1896 and in 1909 they built their only aviation engine, a water-cooled 4V.
-It was presented at the Paris Air Show in 1909. The explosions occurred separately every 180 degrees.

“Mors logo”
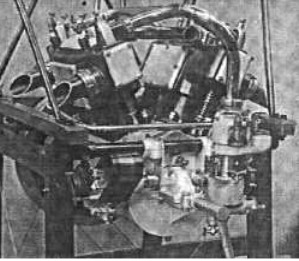
“Mors”
-Cylinders and chambers were cast in one piece. It had free intake and controlled exhaust valves.
-It had 110 mm bore and 130 mm stroke.
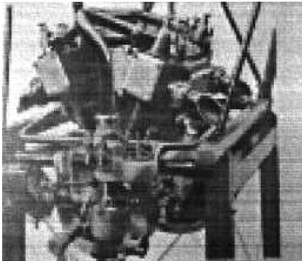
"Another view of the Mors engine"
-It gave 45 CV at 1,600 rpm with a compression of 5 Kg/cm2. The weight was 103 Kg, without water nor radiator.
From Appendix 7: The Petit Duc's engine was inspired by aeronautical architecture. It gave 4.5 CV.
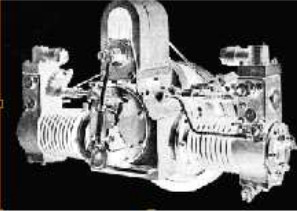
“Mors two-cylinder boxer” (PiP)
From Appendix 12: Line Drawings of the Mors Air-Cooled V4 Engine.
We found them in an aeronautical publication without specifying on which machine it was installed.
-That's why it appears here now.
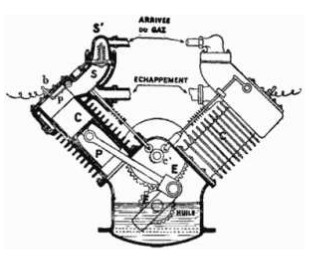
“Front view cross-section"
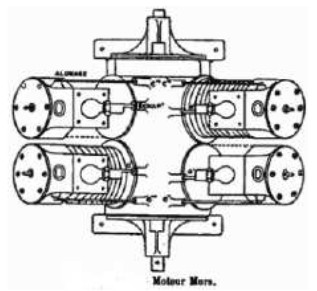
“Top view drawing”
Engines of MORS
Model: 2 cyl. flat twin
Arquitecture: 2-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 4.5 CV
Weight:
Model: V4, 45 CV (Water and air)
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder V-Engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement: 250 cu. in.
Bore / Stroke: 110 x 130 mm
Power: 45 CV @ 1600 rpm
Weight: 103 Kg

"Mors V4"


