Updated: 21-Nov-2022
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm is the result of joining Messerchmitt-Bölkow with Hamburger-Flugzeubau in 1969.
-MBB manufactured helicopters and in the field of engines it built rockets, pulse jets, etc.

“Messerschmitt type pulse jet”
-The MBB-016 pulse jet engine was the first model giving 36 Kgf of thrust and weighing 10 Kg running on JP-4 or JP-5 fuel.
-The one shown is a valveless pulse jet.
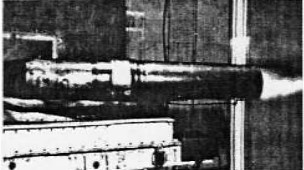
“Solid ram-effect rocket engine”
-In rockets MMB made a family of solid-fuel rocket engines like the one photographed, taking advantage of the ram effect.
-For the propulsion of storable missiles, high-energy solid fuels such as boron or medium-energy, made of compound grains such as UDMH and MMH, were used.
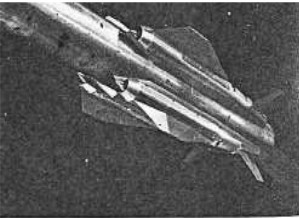
“Missile with ram-effect rocket engine”
-It had frontal air inlets through which the oxygen was supplied.
-They are rocket engines with the ram-effect air acting as thrust augmenter by being heated through the heat of the nozzle and so accelerating its speed.
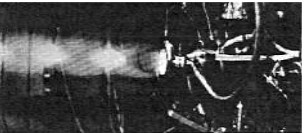
“MBB rocket engine in pulse mode, generating ‘diamonds’ ”
-The MBB that gives 680 Kgf of thrust, runs on H2/O2 and which we see above in pulse mode at 7 Hz.
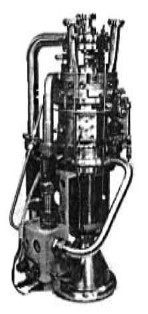
"Liquid fuel rocket"
-Other rockets like the one shown that gives 49 kN at sea level run on liquid oxygen and kerosene. They are considered high pressure.
-The L-7 engine used N2O4/MMH giving 2,800 Kgf in vacuum. It was built from 1996 to 1998.
-The ATC-500 was more powerful with 45,000 Kgf of thrust. For the Beta vehicle it used LOX/LH2.
-Since 1973, MBB has collaborated with SEP to develop the HM-7 for the Ariane's third stage. This engine ran on LH2/LO2 and gave 60 kN of thrust.
From Appendix 6: For the Europe rocket of ELDO, the previous organization of the current ESA, in its Blue Streak version as the first stage and in the second stage the Cora 2 (Coralie made in Germany by MBB and ERNO), and for the third the Astris engine, shown below, was made.

“Astris engine”
-The Astris used Aerozina (a mixture of hydrazine and UDMH) and nitrogen tetroxide, with a little more than 5,000 lbf of thrust (23,300 kN) and for a burning time of 330 seconds.
-Its first launch was in 1964, although it seems that it had several failures and the Europe program was canceled in favor of the new Ariane program.
-Many rocket engine projects were carried out at MBB's Ottobrun factory in Munich, including tests with high-energy fuels such as hydrogen with fluorine.
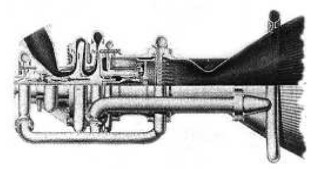
“MBB H-20”
-In 1972 two other MBB high-energy rocket engines were shown, but they were built and tested in conjunction with Rocketdyne. They delivered about 13,000 Kgf of thrust.

"MBB engine pressure chambers"
From Appendix 9: There appear the L-7, ATO-500 rocket engines in this brand.
Engines of MBB
Model: ATC-500 (ATO-500)
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: H-20
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: L-7
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Pulsejets
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Ram-rocket engine
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Ramjets
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Rocket engines
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:


