Updated: 15-Apr-2020
In 1908, French engineer René Lorin exposed the concept of an intermittent impulse jet engine.
It was actually an orthodox six-cylinder piston engine, with the exhausts all directed in one direction.
-All exhausts had a convenient diverging shape.
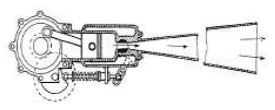
“Lorin engine”
-At the moment of expansion the exhaust valve was opened so that the exhaust exited at high speed through the nozzle.
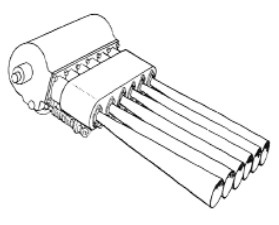
“Full aspect”
-Intake, compression and combustion strokes occurred normally, only the exhaust one was advanced to take advantage of the available gas energy.
-The thrust was insufficient and the engine has remained occupying only an important place in engine history.
-In 1913, Lorin did studies on thermal conduits acting as ramjets, perhaps a predecessor to those that would be made later.
-They were called "Lorin's Nozzle" and have been used as an example in theory classes.
-Still in 1915, when he was an Artillery Officer, he proposed an aerial torpedo to bomb Berlin, which was rejected by the French authorities as it was considered unfeasible.
From Appendix 6: From an old publication we now have the simplest outline of his propulsion idea.
-The concept is to force a part of the explosion energy in one direction to create thrust. Rocket principle.
-A more advanced and more plausible version appears in the main text.
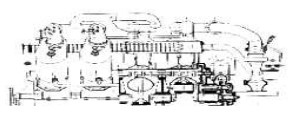
“Lorin's concept”
From Appendix 7: Rene Lorin (1877-1933) was trained at Lycée Henri IV and at Ecole Central he became an engineer in 1901.
-While in the Angouleme bus company, he became interested in aviation, the new mode of locomotion.

-He was a pioneer in propulsion studies, but without propeller. He presented patents that he even sent to Chanute. Later, Leduc would recognize his genius.
-In 1910 he presented his "Torpille Aerien". Precursor of thermojet engines such as ramjets and pulsejets.
-He presented the continuous-flow engine to the French government in 1914 and the pulsating one in 1915. It was installed on a remote-controlled device capable of reaching Berlin.
-Between 1914 and 1918, he promulgated a small turbine called "Airelle".
-He wrote a beautiful book entitled "L’Air et la Vitesse" with great precision in his expressed ideas.
From Appendix 12: The concept of jet propulsion designed by Lorin is clearly seen in the below drawing. The exhaust valve empties into a rear-facing nozzle.
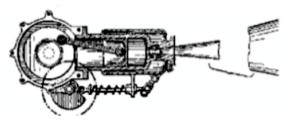
“Lorin's reaction engine”
Engines of LORIN
Model: Airelle turbine
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:
Model: Piston engine with exhaust jet
Power: Other details:
Model: Pulsejets
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:
Model: Ramjets
Arquitecture:
Chambers:
Fuels:
Feed System:
Ignition:
Thrust:
Weight:


