Updated: 13-May-2020
Through TsIAM he developed a type of "accelerator" or a compressor driven by a piston engine ( Klimov VK-107A, or M-197A).
-It consisted of a 3-stage compressor that sent the air and it is said that the exhaust gases of the piston engines went through the water radiator to a chamber with seven injectors that increased the speed with a thrust of 660 lbs
-It was the Khalschevnikov VRDK.

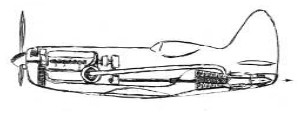
“I-250”
-Ity was tested on I-250 prototypes and on the I-300. In the photograph we see the exhaust outlet through the tail cone opening.
“VRDK schematic drawing”
Sometimes written as Kolchevnikov (see also).
From Appendix 10: During WWII this engineer together with Feedev made a plane powered by a traditional engine (VK-107R) that drove a traditional propeller with a post-burner as a motorjet. Project E-3020. (see chapter M-).
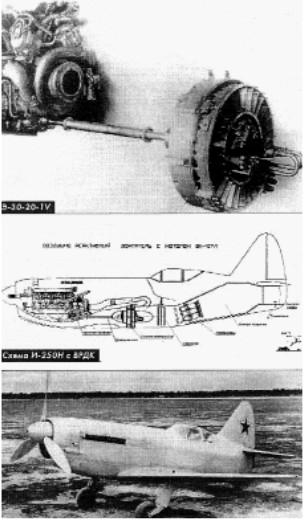
“El proyecto E-3020”
-A compressor driven by the main engine (above) introduced pressurized air into a rear chamber as a post-combustion to produce an increase in thrust.
-The gained speed was not compatible with weight gain and exaggerated fuel consumption. This plane was the I-250, It seems that there were derivatives like the one in the previous graphic and also an I-320.
Kholshchevnikov (English literature) also written Khalschevnikov (Spanish literature). See both chapters.

“Designer Konstantin Vasilievich Kholshchevnikov”
Engines of KHALSCHEVNIKOV
Model: VRDK ( I-250 & I-300). Motorjet
Arquitecture:
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: / ---
Weight:


