Updated: 13-Feb-2019
Guiberson was the founder of the "Guiberson Diesel Engine Co", in Dallas, TX.
The designs (at least of the first engines) are from the Austrian engineer based in USA F.A. Thaheld. (1930s)
-In the early 1930's, Guiberson began to build Packard Diesel engines.
-Actually, Diesel Packard single-valve engines came from the Austrian engineer Thaheld. (A-980 engine) but Guiberson managed to increase the power from 185 to 220 hp (DR-980).

“Guiberson A-980”
-The A-980 is a Diesel engine from 1932 that gave 185 hp and had 9 air-cooled radial, single-valve cylinders,.
-Also known is the single-valve A-918 engine from 1934. It gave 250 hp with an identical architecture as the one mentioned before. It had 9 air-cooled, radial cylinders. Other information gives 253 hp at 2,100 rpm.
-The A-1020 model was an improved model that gave 310 HP with the same construction formula. Except that the valves become classic: one for intake and another for exhaust.

“Guiberson A-1020”
-This engine obtained its Type Certificate in 1939/40, the ATC-220. It had a total displacement of 1021 cu. in.
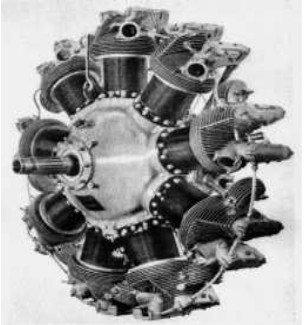
“A-1020”
-Because of war needs in WWII Guiberson had to build tank engines (model T-1020) with 210 hp and the T-1400 model that gave 250 hp. It is mentioned that they are a Buddha Co. conversion for light tanks.

“Motor Guiberson, observed”
-The 9-cylinder A-1020 with mechanical supercharger, had 16.73 liters of total displacement and a compression ratio of 15 to 1. It gave 340 hp at sea level without supercharging.
-Due to the high compression ratio, starting was done with Coffmann cartridges.
-A 7-cylinder radial version is also known. It gave 310 hp.
-There was another engine from 1942. Could it be a C-? It was a horizontally-opposed, 6-cylinder engine made for a military contract. It would use the same cylinders and pistons as the radial engines
-The main text mentions three Guiberson radial engines, the A-918, the A-980 and the A-1020.
-Only the last two are provided in the text, below we show a photograph of the A-918 that has been obtained.
-It is a nine-cylinder, giving 240 hp at 2,020 rpm. It has single-valve cylinders.

“Guiberson A-918”
From Appendix 6: Side view of the radial diesel engine that was the first to obtain a license from the American government to be installed on an airplane.
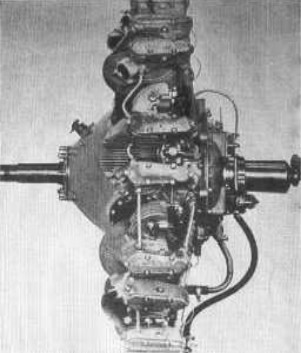
“Side view of a Guiberson Diesel engine”
-As we know, the lower consumption of the diesel engine compared to another gasoline of the same size, gives the aircraft greater range with the same fuel tanks.
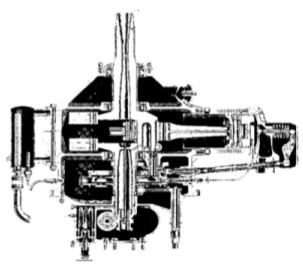
From Appendix 12: The A-980 engine can be considered a prototype. It was the first Diesel engine that had a single-valve cylinders. The engines that followed, had two valves per cylinder.

“El Guiberson monoválvula, cutaway”
-It was designed in 1932, and was very similar in concept to the Packard Diesel in the same period.
-Precisely, working with only air in the intake process, allowed to use the same valve for the exhaust.
-That is so because during the two phases, the exhaust (approx 180°) and the next, the intake, (another 180° approx.), the valve was kept open for 360° approx.
-In the exhaust process the piston rises, expelling the gases out of the cylinder head at the rear. Then the intake stroke began, lowering the piston and drawing atmospheric air only through the front intake duct. Both intake and exhaust ducts were communicated during the compression and combustion strokes (the other 360 °).
-In these moments the air circulates freely entering through the intake duct into the cylinder head, cools the valve and exits through the exhaust port freely. This influences the advance of the plane.
-See the following illustration in which we can see the details of this explanation. In theory, it was very effective. In practice, the free exhaust gases went to the cockpit in the monomotor.

“Details of the above explanation”
-The advantage of Diesel engine was lower consumption with cheaper fuel. On the other hand there was the loss of immediate power at higher altitudes if it was not a supercharged engine.
-The aviation radial Guiberson in its variant of the T-1020-4 was used in land vehicles such as the Stuart M3 tank from 1936.

"Photo of the T-1020-4 at a Military Museum"
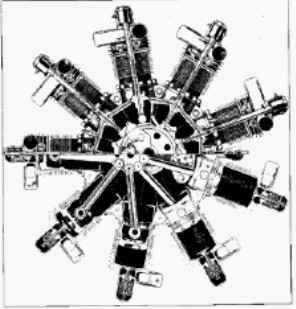
-New illustrations for this American brand of Diesel radials.
“Guiberson 9-cylinder cutaway”
“Connecting rod system”
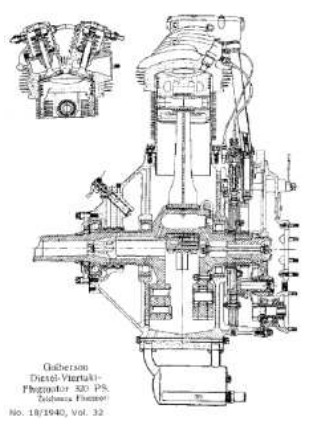
"Guiberson Diesel cross-section from Flugsport"
Engines of GUIBERSON
Model: A-1020
Arquitecture: 4-stroke9-cylinder Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement: 1021 cu. in.
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 350 HP
Weight:
Two valves

"Guiberson A-1020 fig.2"
Model: A-918
Arquitecture: 4-stroke9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 250 HP @ 2100 rpm
Weight:
Single-valve

"Guiberson A-918"
Model: A-980
Arquitecture: 4-stroke9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 185 HP
Weight:
Single-valve

"Guiberson A-980"
Model: T-1020, T-1020-4 tank,
Arquitecture: 4-stroke9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 210 HP
Weight:
Model: T-1400
Arquitecture: 4-stroke9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 250 HP
Weight:


