Updated: 19-Nov-2018
In 1914, Professor H.F. Fullager proposes a 2-stroke engine with opposed pistons in twin cylinders, and two crankshafts.
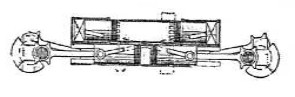
"Fullager principle”
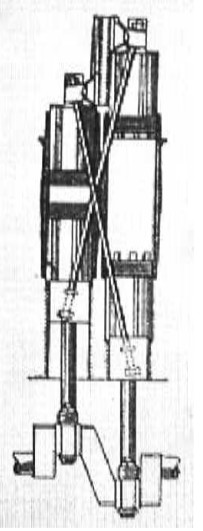
“Fullager engine”
-Each pair of cylinders forms an engine module, naturally expandable.
-The pistons of the upper cylinders are connected to those of the lower ones by means of crossed rods.
-The idea is great, because while some evacuate others compress.
-With 8 cylinders and 16 pistons it was planned to reach 750 CV at 2,200 rpm.
-It was not installed on any aircraft while remaining experimental.
From Appendix 6: The new information that has been obtained about this engine is called "Fullagar" erroneously. From H.F. Fullager
-The illustration that goes with it, shows the engine from another angle so we can see the crossed -oblique- piston-rod system, the double pistons and crankshaft much better. This gives us a clearer idea of how the engine works.
Engines of FULLAGER
Model: hor. op. 8 cyl, 16 pist.
Arquitecture: 2-stroke8-cylinder Opposed piston engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 750 CV @ 2200 rpm
Weight:
It has 16 pistons in 8 cylinders.


