Updated: 05-Sep-2018
From the year 1909. This air-cooled engine, the most significant of the brand, consisted of two groups of four cylinders in cross, with double pistons and the rods were fixed to the center of these pistons.
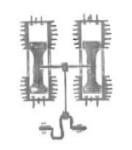
"Favata principle"
-The crankshaft was in the center, between the groups of cylinders that were in radial arrangement. They could be grouped into 1, 2, 4 cross elements, depending on necessity.
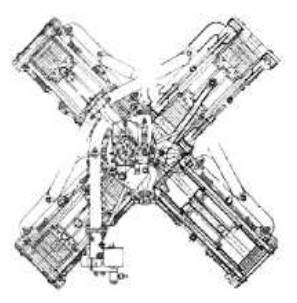
"Favata X-engine schematics"
-Favata is known to have started building a classic 4-cylinder inline engine, and another 8-cylinder V-engine.
-View of the eight-double-cylinder engine that gave 180 CV.
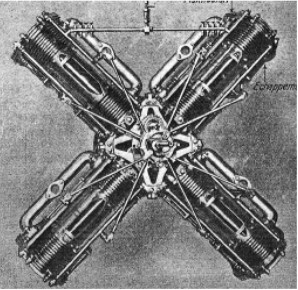
"16-cylinder Favata engine"
-At the Paris Air and Space Museum in Le Bourget, and in the engine stock, there is a Favata model with four horizontally-opposed cylinders, where we can see very clearly the junction of the connecting-rod to the pistons of the two adjacent cylinders.

"Favata double 4-cylinder at the MAE"

"Connecting rod between Favata cylinders"
From Appendix 10: Below we show new photographs to investigate its construction in detail.

"Front view of an Favata at an exhibition"
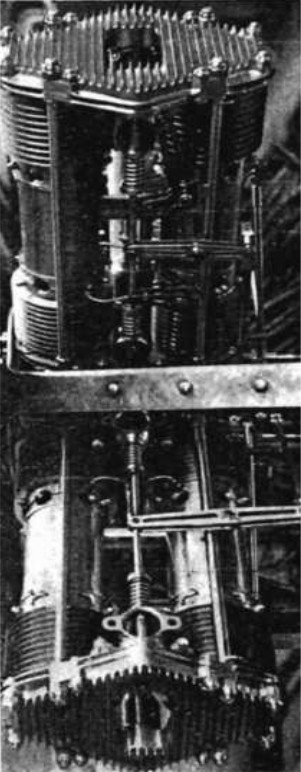
“Favata engine side-view with double-piston cylinders”
Engines of FAVATA
Model: 16 cyl. X (4x4)
Arquitecture: 16-cylinder X-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"Favata 16-cylinder"
Model: 4 cyl, X
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder X-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: 4 cyl. boxer
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder Horizontally opposed
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: 4 cyl. inline
Arquitecture: 4-cylinder In-line
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:
Model: 8 cyl X (2x4)
Arquitecture: 8-cylinder X-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 180 CV
Weight:
Model: 8 cyl. V
Arquitecture: 8-cylinder V-Engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:


