Updated: 15-May-2020
This company built aircraft as well as engines, starting under license with the Wright Cyclone, Lorraine 12b and Siemens Sh-14.
-Afterwards, national-design, 9-cylinder engines appeared, known as "El Gaucho" and "El Indio". They also produced other small piston and rocket engines.
-It is known as FMA like Mexico, but with a different meaning (Airplanes instead of Aviation) See.
-In 1927, the Military Aircraft Factory was founded in Córdoba (Argentina) to build aircraft and engines. The first engine was the French Lorraine-Dietrich 12b 12-cylinder, W-engine that gave 450 CV.

"It is stated as the first aviation engine in South America. Year 1929"

"FMA technical staff, engineers and operators next to the first built engine"
-The chief engineer of the project was Antonio Taravella, possibly behind the engine, with a tie.
-It was not until 1935 when they made a new engine, the Wright R-1820, also under North American license. The same as the German Siemens Bramo engine (1938), but this one was installed on the FW-44-3 airplane, possibly for training.

"The Siemens more closely" (A-Z)
-We are in 1943 when a new era began for the FMA factory, the most interesting because they started to design their own engines.
-It is the I.Ae-16, "El Gaucho" engine with 9 radial cylinders giving 450 CV. It was installed on the DL-22 training aircraft, which looked amazing with the American "Texan" T-6.

"El Gaucho" at the Aeronautical Museum of Argentina"
-In 1947 appeared "El Indio", model I-Ae-19, much more powerful, with 9 radial cylinders and in three versions, the normal without gear and with gear.
-Giving 690 CV and the supercharged version 750 CV.
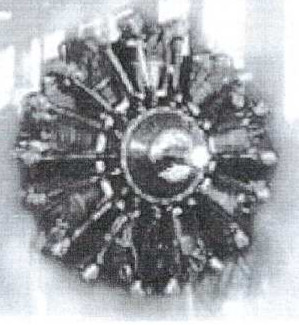
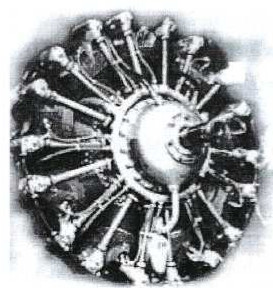
”El Indio, without and with gear” (A-Z)
-In this final part referred to the Argentine FMA we come to the year 1948 in which the Rolls-Royce "Nene II" and "Dervent V" are built under British license with a view to the "Pulqui I and II" jet aircraft. This is stated in the publication "The Aerospace Engines, A-Z" and on the website of the Aeronautical Museum of Argentina. These aircraft were designed by Kurt Tank (notable German engineer during WWII).

“El R-R on a Pulqui” (FMA-RR?)
-Hörten, another German engineer designed the "Pulqui III" known as the "Argentine Mirage" with delta wing and supersonic speed, on which two Bristol-12 "Orpheus" or one RR "Avon" engines were planned. After interrupting his collaboration in Argentina, Kurt went to India where he completed the "Pulqui III" project at Hindustan Industries with the "Marut" aircraft. It is not known whether the Bristol or the R-R Avon have been built at by FMA, since in 1948 the Reaction Engines Division was created.
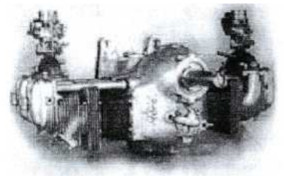
"FMA I.Ae O-1600"
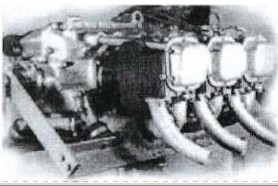
"FMA I.Ae O-4000"
-Two unknown engines have been the horizontally-opposed cylinder ones for general aviation. They have transcended two models: the 4- and the 6-cylinder. The upper one is the 4-cylinder that gave 65 to 75 CV with gear. The lower one is the 6-cylinder giving 160 CV.



“Pulsejets without and with valves”
-In the year 1955, FMA tests with reaction engines began, ramjets and pulsejets with and without valves. The upper is one of the Lockwood-Hiller type (see A-Z), the middle one a variant of the former one, and the lower one is of the type that was used on the German V-1.

"Launch base with Castor and Rigel"
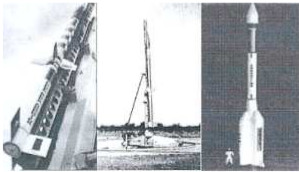
"Two Taurus and the satellite carrier Alacran + Condor"
-Liquid fuel rocket engines were made for high-altitude probes and for cruise-type missiles such as the "Tabano", due to engineer Ricardo Dyrgalla. Then there was a great series of solid rockets. A list may be the following: Judi, Orion I and II, Canopus I and II, Castor, Glag I and II, Dim, Rigel and Higel, Apex (Alpha and Beta), Centaur, Scorpion, Condor, etc.
-It is known that, eventually, FMA became Lockheed-Martin Argentina SA.
Engines of FABRICA MILITAR DE AVIONES
Model: ”El Gaucho” I.Ae-16
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"El Gaucho at the aeronautical Museum in Argentina"
Model: ”El Indio” modelo I-Ae-19
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

""El Indio" engine with gear"
Model: Lorraine 12b, 450 CV (1er motor fabricado) (Lic.
Arquitecture: 12-cylinder W-engine
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 450 CV
Weight:

"Lorraine-Dietrich 12b"
Model: Siemens Sh-14 (Lic.)
Arquitecture: 7-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"FMA Argentina, Siemens engine"
Model: Wright Cyclone (Lic.)
Arquitecture: 9-cylinder Radial
Cooling: Air
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:


