Updated: 12-Feb-2020
The Chrysler Corporation, Detroit MI, a car factory, which today is Daimler-Chrysler.
-In the WWII war effort they built large quantities of R-3350 engines and later the P&W J-48 as well. The T-36 turboprop was canceled in 1948.
-Chrysler was invited by the US Army to develop more powerful engines to be installed in the XP-47H. The proposed engine was the IV-2220.
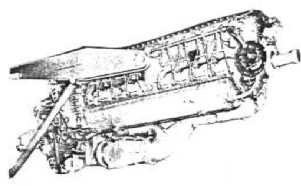
"Chrysler IV-2220"
-It was a liquid-cooled, 16-cylinder inverted Vee engine with gear and a two-stage supercharger.
-Therefore it had an intercooler or heat exchanger for cooling the intake air below the engine.
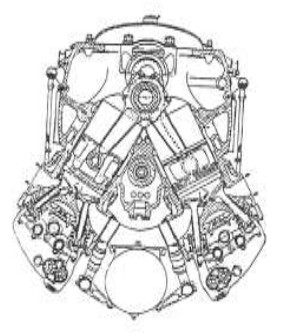
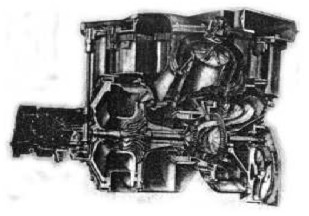
"IV-2220 Cross section"
-Later, this great engine was renamed XI-2220-11. It had a CH-5 General Electric turbocharger, and delivered 2,500 hp. Flight tests were made from the Wright Field.

"Chrysler IV-2220"
-Below we show a new view of the XI-2220 model, a 16-cylinder inverted 60° Vee engine that was liquid cooled and turbocharged (-11).
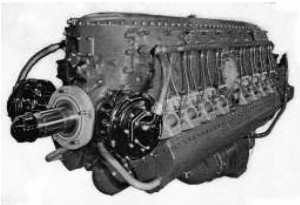
"Chrysler XI-2220"
-Furthermore and more recently the West Bend Division that made small industrial Chrysler engines entered aviation again, in the field of ULMs and RPVs.
"West Bend"
-The 820 outboard model was converted and gave 8 to 10 hp. Except the Power-Bee that delivered 12 hp at 8,000 rpm and at 9,800 rpm in aviation installations.
-There have been two-stroke, single-cylinder engines with a displacement of 134 cc. Twin installations have been made like the Twin-Powers, Twin-Maximizer and Dyad.
-From the five available types of West-Bend, 500, 580, 610, 800 and 820 series, the last one is chosen.

"3 Chrysler logos"
-The Chrysler Design Department realized the project of a 1,000 hp turboprop known as A-86, which the Navy classified as XT-36.
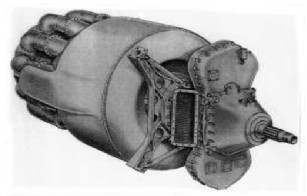
"A-86-D2”
-It has certain features of the Bristol "Theseus", which also used the "heat recovery" system having the exhaust gas causing to spin a rotary honeycomb that transferred the heat to the admission duct prior to chamber inlets.
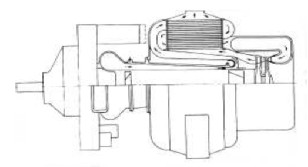
"XT-36-D2"
-In this schematic longitudinal cross section we see that the drum of the illustration below is rotating inside the engine in the exhaust outlet zone. Through the outside and inside of the thousands of thin tubes, the air coming from the compressor recovers a part of the heat that otherwise would be lost into the atmosphere.
-Four of these illustrations are gently used on behalf of AEHS.
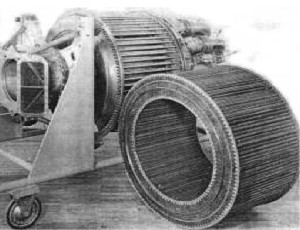
"Rotating drum"
-Chrysler already used this heat recovery system in its experiments with automobile turbines, as we can see below in the A-831-2 engine cutaway drawing. The difference is that here there are two rotors, one on each side. This engine delivers 130 hp at 45,700 rpm.
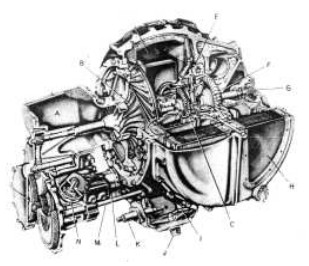
"Chrysler A-831-2"
-But Chrysler began the turbine issue with other models such as the CR-2, which we show as well. This engine had heat recovery and was fitted in a Plymouth Belvedere with which has been made a US journey from coast to coast to demonstrate its ability.
"Chrysler CR-2"
-We see the single combustion chamber system with the heat recoverer horizontal above the engine. In trials they introduced a turbine distributor, a stator with vanes of variable incidence, which produced significant fuel savings.

"From New York to Los Angeles"

"Chrysler XT-36-D2"
-In the latest shown version of the XT-36-D2 we see the fasteners on the forward ironwork and through a tubular bed, to the firewall.
From Appendix 6: The large aircraft engine that was made by this well known automaker during WWII was due to the search for greater powers. It was the XI-2220.
-We now show a diagram of the engine's inner distribution, noticing the originality of some devices like the power output transmission at half the crank length by a smaller cogwheel gearing a greater one to reduce propeller speed.
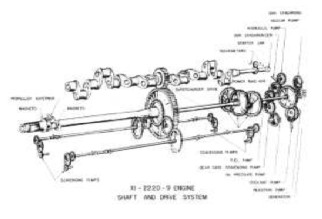
"Distribution gear diagram"
-The above illustration has been extracted from the manufacturer's technical documentation, via AEHS, like the picture below, which shows the engine on a bench for testing.

"XI-2220 during testing"
-Around 1976, the Argentine Cicaré CH-3 “Colibrí” helicopter has been tested with an adapted Chrysler car engine. It was the eight-cylinder Vee engine that had a power output of 150 kW. It ran on gasoline.

"The Cicaré Colibrí with Chrysler V8"
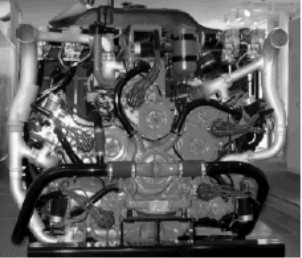
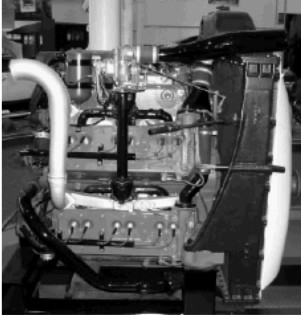
-We take this opportunity to include in the extension of this chapter a curious Chrysler engine group consisting of five six-cylinder, inline, automotive engines coupled by means of a front gear box
-Initially these engine groups were intended for powering tanks, not ruling out aviation applications.
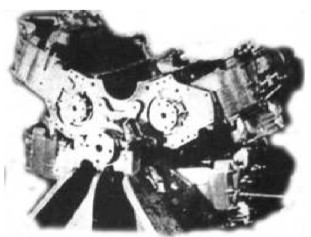
"Four engines, the fifth to be installed"
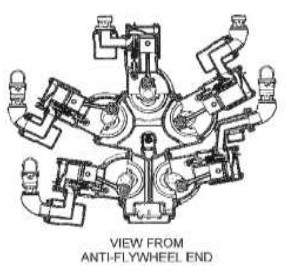
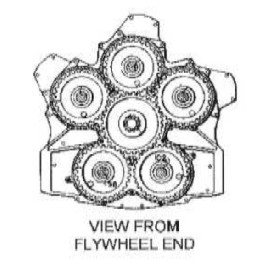
-Through AEHS in Alabama we have obtained more details of this engine that appears mutilated in the photo above as the fifth six-cylinder engine is missing.
-We have three drawings: the one of the outer assembly in which we see a fan in front of everything. The one with the coupling of the five engines in a diagram, and the one with the gear assembly that joins all of them on a central power output pinion.
"Aspect of the engine grouping"
"Arrangement diagram"
"Power joining gear assembly"
From Appendix 9: Car manufacturer that built a special inverted Vee engine for high-power aviation. (See main text).
-There is an engine of this brand that, although it seemed to have been intended for aviation use, was installed in an armored tank. Somewhere in this publication this engine or engine idea appears. This engine has now been identified as the Chrysler A-57 "Multibank".
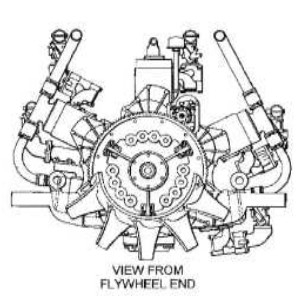
"Chrysler A-57, rear view" (AEHS)

“Power joining gearbox” (AEHS)
-The five peripheral gears correspond to the five 6-cylinder inline engines in addition to the central gear of the transmission output.
-In the picture below we can see two of the side engines.
“Multibank side view” (AEHS)
From Appendix 10: During WWII they made an interesting engine (see main text), the IV-2220 (36 liters total displacement).

"Chrysler IV-2220" (Photo Bob Scott)
-It was a big 16-cylinder inverted V engine (maybe two 8-cylinder engines coupled in V, in theory).
-It was tested on the XP-47 Thunderbolt to get more performances in order to intercept the German Me-262. It had a GE compressor horizontally installed under the engine between the two cylinder blocks.
-What is calling our attention, is that the ignition sequence does not coincide with any Vee-engine. Counting the cylinders from front to rear and being the right side R (always from the pilot's seat) and L the left, we have the following firing order:
-1R-4L-5R-2L-7R-6L-3R-1L-8R-5L-4R-7L-2R-3L-6R- 8L. Just as noted on the rating plate.

“Chrysler IV-2220 engine plate” (photo Marc Rozman)

“Testing the Chrysler engine” (photo Allpar.com)
-Mechanically supercharged 16-cylinder inverted V engine.
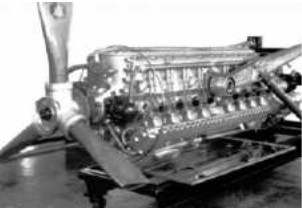
"The engine at the Chrysler Museum"
-Now the cross-section we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter. It was a WWII project.
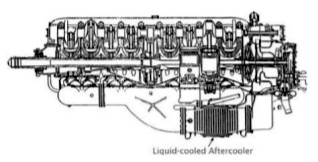
"Chrysler aviation engine cross-section"
-Thanks to this cross-section we see the intercooler that does not appear in any previous illustration including those of the main text.
-During WWII, in the war effort, they made Wright engines under license. Specifically the R-3350.
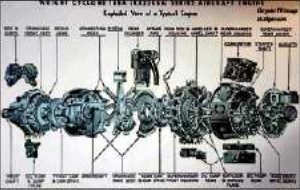
"Exploded view for the Wright R-3350"
-Other automotive brands such as Dodge, Buick and Nas-Kelvinator also powered the Pratt and Whitney or Wright, at that time.
Engines of CHRYSLER
Model: A-86 (XT-36)
Arquitecture: Turboprop
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust: 1000HP / ---
Weight:
The Chrysler Design Department realized the project of a 1000 hp turboprop known as A-86, which the Navy classified as XT-36.
Model: IV-2220 (XI-2220)
Arquitecture: Inverted V-engine
Cooling: Liquid
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 2500 HP @ rpm
Weight:
With gear and a two-stage supercharger.

"Chrysler XI-2220"
Model: PW, J-48 (Lic)
Arquitecture: Turbojet
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
In the WWII war effort they built this engine under license.
Model: T-36
Arquitecture: Turboprop
Compressor/s:
Combustion chambers:
Turbines:
Power / Thrust:
Weight:
The T-36 turboprop was canceled in 1948.
Model: Wright, R-3350 (Lic)
Arquitecture: Radial
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: @ rpm
Weight:
In the WWII war effort they built large quantities of Wright R-3350 engines.


