Updated: 30-Jan-2020
In 1928, Louis Breguet, a remarkable aircraft manufacturer, acquired from the famous Ettore Bugatti car brand, the license to build the 16C engine for his own aircraft.
-A duplicate of the same engine, with two cylinder blocks of two 8-cylinder engines (total 16 cylinders) in parallel, gave way to the 16D that delivered 600 hp with a front gearbox.
"Bugatti drawing"
"Coupling and reduction gear"
-On top of a double-crankshaft crankcase they placed the two cylinder blocks that gave the engine a "U" shape.
-For all engines, if one row of cylinders stopped, these cylinders could be isolated, and the rest of the cylinders would keep on running.
-Declutching is done automatically. The cylinders have four valves each, and dual ignition.

"16-D, rear view”
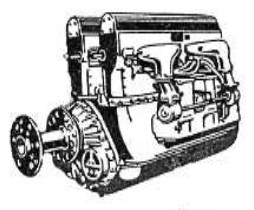
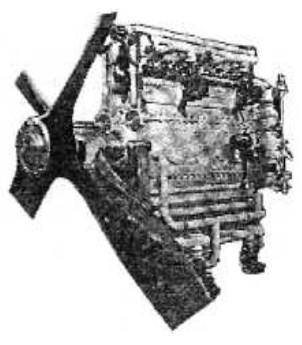
-The "U-24" version was a row of eight cylinders above the central block and another row below it. The engine had a power output of 600 hp at 2,800 rpm.
-The U-24bis variant hardly differed.
"Breguet- Bugatti U-24"
-The "32-A" consisted of two 16-D engines coupled front to front, offset in height with a central coupling box. It had an output power of 850 hp.
"32-A"
-Installed on the Breguet XX "Leviathan", the mechanic could walk around the engine during flight, as the engine was fitted in a sufficiently large nacelle. There were 32 cylinders in total.
-The 32B was similar to the 32-A, but with double U engines, one upright U on top of the central crankcase and an inverted "U" below it.
-The engine called "Quadimoteur" basically was a 32-B that gave 950 hp at 2,100 rpm. (H-32-B).
"Quadimoteur"
-In the picture below we can see the Breguet-Bugatti "Quadimoteur", as exposed in the Air Museum at Le Bourget.
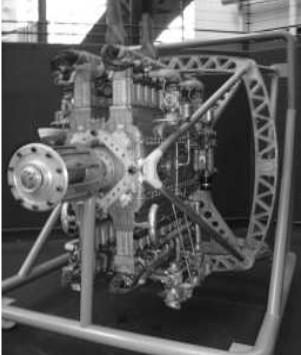
"Quadimoteur”
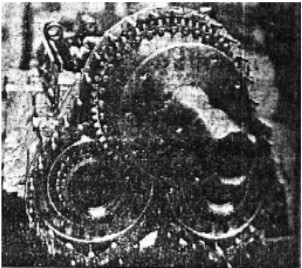
-We clearly see the four rows of eight cylinders and the four crankshafts around the single output shaft. (See main text).
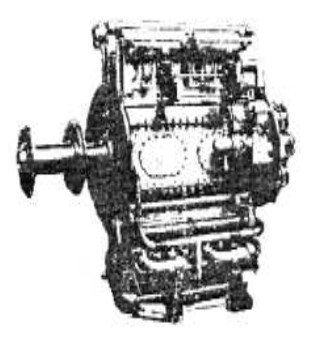
-A simpler engine was the 500 hp Breguet-Bugatti 34.
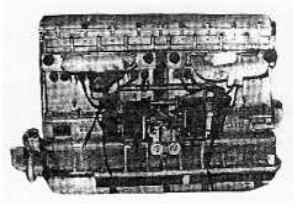
"Breguet - Bugatti 34"
-In the US, the Bugatti engine was manufactured by Duesenberg that built famous high-quality cars like the King-Bugatti. (See Bugatti).
-From appendix 6: At the 1919 Paris Air Show, Louis Breguet presented two engines.
-A rotary engine with variable compression, made under Damblanc-Mutti license.
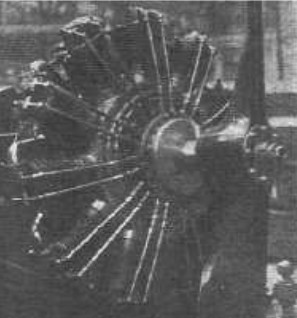
"Breguet (Damblanc)"
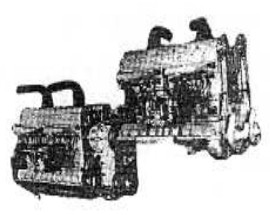
-The other engine was rather a group of two Bugatti engines built by Breguet itself. They were installed in tandem and with offset in height to allow the shafts pass through the front engine.
"Breguet tandem"
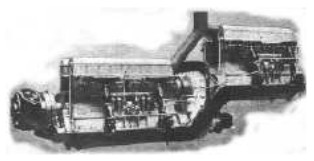
-Between both engines there was a gearbox that added the power of both engines through clutches so that if one engine failed, it did not prevent the other from running on.
"Breguet-Bugatti CV.450"
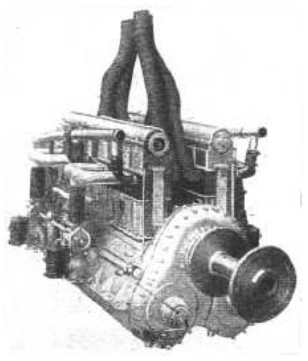
-For the big Leviathan aircraft of that time, France proposed a large complex or compound motor, the Breguet-Bugatti 32A consisting of two U-model tandem aircraft engines of the same brand.
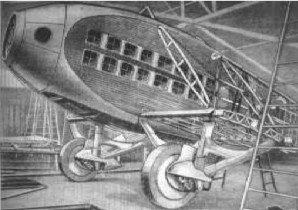
"Leviathan drawing"
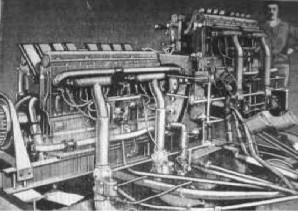
"32A, an engine of considerable size"
-The two engines are facing each other, and in the central part of the assembly there are the gears that join the four crankshafts on a single large pinion, reduction gear together with the output shaft for the propeller.
-This shaft passes through the front engine between the two U-forming cylinder rows.
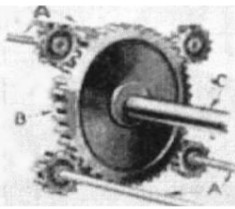
"Main gear principle"
-This is not explained in the main text. In some way it is the same solution that Fiat has for the large compound AS-6 engine fitted on MC-72 aircraft.
From Appendix 10: New picture for the “Quadimoteur”.
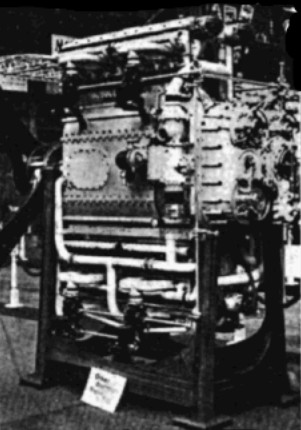
"Breguet composed by 4 Bugatti 8-cylinder engines"
Engines of BREGUET-BUGATTI
Model: 34

"Breguet - Bugatti 34"
Model: Breguet (Damblanc lic.)

"Breguet (Damblanc)"
Model: H-32A

"32A engine, considarable size"
Model: H-32B
Model: Quadrimoteur

"Breguet-Bugatti - Quadrimoteur"
Model: U-16
Model: U-24

"Breguet- Bugatti U-24"


