Updated: 28-Jan-2020
They made a toroidal engine with the same principle as we have seen with Baradat-Esteve (the 4-piston engine), and with Dewandre, etc. In 1910 he introduced the 75 hp, double-toroidal engine shown in the illustration below.

"Beck module"

"Beck double semi-toroidal"
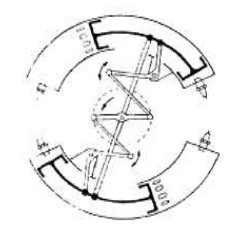
"Beck study diagram"
-The two opposed double pistons oscillated, linked together by a direct connection, while the piston reciprocation, by means of levers and connecting rods, was transmitted to the crankshaft as continuous rotation.
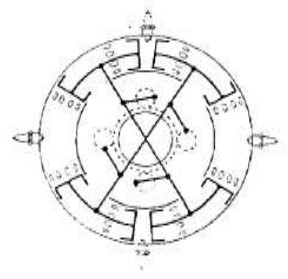
"Dewandre, comparison"
-Apparently the same, the Dewandre engine uses small gears that are driven by small crankshafts, and connecting rods.
-With the 4-piston engine, the connecting rods dit not drive the crank shaft directly, but they did it through an ingenious coupling of levers to a single rod as shown in the illustration below.
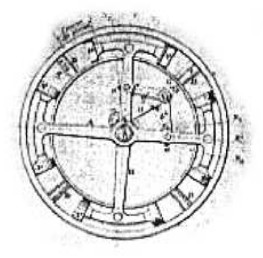
"Beck realistic diagram"
-Finally, the uncovered Beck, wherein we can see the pistons and their toroidal arrangement.
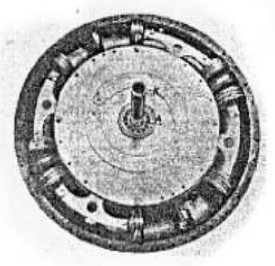
"Uncovered Beck"
-Below we show an image of the engine with opposed pistons in a toroidal body that transmits its movement to a rotating shaft by connecting rods and rocker arms .
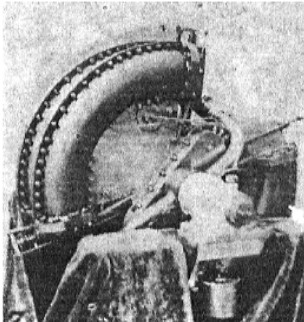
"Semi-toroidal Beck engine"
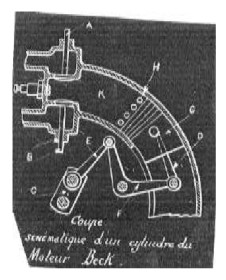
"Beck blueprint details"
From appendix 6: At the 1910 Paris Air Show they presented the double-body Beck engine. This time with more details.
-It had a relative small size and gave 45 CV.

“Double-body Beck engine” (PiP)
-Here we have a new illustration of the 50 hp toroidal Beck engine. It is composed of 8 curved cylinders in a double toroidal body with reciprocating pistons.
-In this new photo more external details are seen. See inner diagram in the main text.
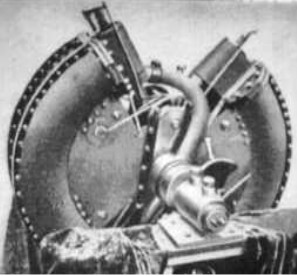
"Beck front view"
From appendix 10: Obtained from the MAE information center. This is an original engine architecture that has some curved cylinders in a circular position. One piston of each cylinder is attached with an oscillating part transmitting their movement to some elbows with rods.
-The rotation is slow, between 200 and 900 rpm. They made three models: Type A with 35 CV, Type B with 50 HP and Type C with 75 hp. These engines were similar to each other except in size and weight, which was different, with the weight corresponding successively to 70 Kg, 80 Kg. and 85 Kg.
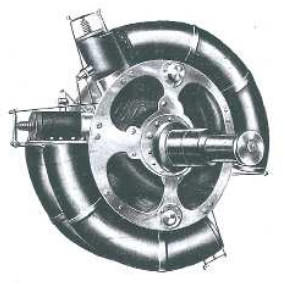
"Beck engine"
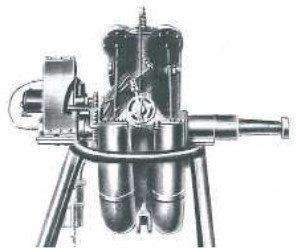
"Side view with the magneto and the half hidden carburetor"
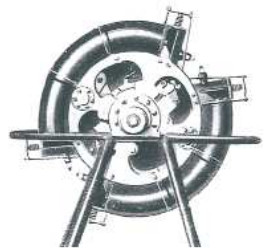
"Front view"
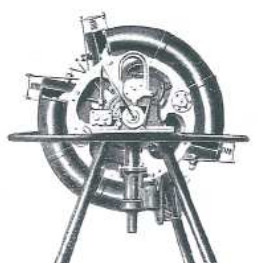
"Rear view"
Engines of BECK
Model: Toroidal, varios tipos

"Beck double semi-toroidal"


