Updated: 31-Mar-2020
In 1910 Ligez made a bi-rotary radial engine that was built with three cylinders at 120° on a cylindrical crankcase. All three connecting rods drove the same crank.
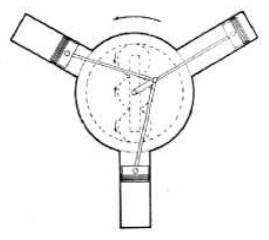
“Ligez 3-cylinder engine schematic drawing”
-This crank, while turning, drives by means of a toothed pinion two other fixed center pinions, which rotate in the opposite direction and internally drive a toothed crown and are invariably fixed to the cylinder block.
-The cylinders rotate as a compact mass in the opposite direction to the crankshaft and under the ratio of 1 to 3 because the development of the crown teeth is three times that of the crankshaft sprocket.
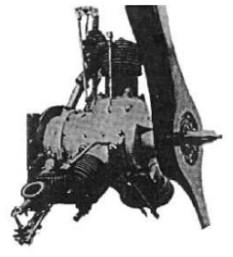
“Ligez 3-cylinder engine”
-So, the crankshaft rotates at 1,200 rpm and the cylinders in the opposite direction at 400 rpm, which gave a relative angular displacement of 1,600 rpm.

“Ligez 18-cylinder engine”
-The opposite rotation of these parts served to counteract the engine's torques and its influence on the plane.
-In 1912, Ligez introduced an 18-cylinder under the same principle. It is documented that it gave 500 CV, something high for the time.
Engines of LIGEZ
Model: 18 cyl. radial bi-rotary
Arquitecture: 18-cylinder Rotary
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power: 500 CV
Weight:

"Ligez 18-cylinder engine"
Model: 3 cyl. radial bi-rotary
Arquitecture: 3-cylinder Rotary
Cooling:
Total Displacement:
Bore / Stroke:
Power:
Weight:

"Ligez 3-cylinder engine"


